A recent study of people with overweight or obesity and osteoarthritis showed that telehealth visits can be an effective way to provide care and may even help with weight loss, which can improve symptoms and prevent OA from worsening: https://t.co/xSSFxJmmfz #HarvardHealth pic.twitter.com/Qzoa7U4reD
— Harvard Health (@HarvardHealth) January 12, 2022
Tag Archives: Studies
Studies: Salt Substitutes Lower Stroke, Death Risks
Covid-19 Vaccination: Risks Of Myocarditis
Given the myriad of cardiac concerns associated with SARS-CoV-2 infection, news that the myocarditis associated with mRNA vaccination is mostly mild and resolves quickly in the rare instances in which it occurs was welcome news. The findings continue to tip scales in favor of vaccination and resulted in this week’s top trending clinical topic.
Brain Research: The Many Benefits Of Healthy Sleep
Brain Study: REM Sleep Behavior Disorder Linked To Neurodegeneration

REM sleep behavior disorder is linked to Parkinson’s disease, a movement disorder; dementia with Lewy bodies, which causes cognitive decline; and multiple system atrophy, in which the ability to regulate involuntary functions, such as blood pressure, breathing, and bladder and bowel function, deteriorates.
ROCHESTER, Minn. — People with rapid eye movement (REM) sleep behavior disorder act out their dreams. While sleeping safely in bed, for example, they might throw up their arms to catch an imaginary ball or try to run from an illusory assailant. Such actions are more than just a nuisance. People with the disorder have a 50% to 80% chance of developing a serious neurodegenerative disease within a decade of diagnosis.
ANALYSIS: COVID-19 VACCINE EFFICACY EXPLAINED (VIDEO)
Recent studies have shown that the effectiveness of Covid-19 vaccines is decreasing, though experts say the shots still work well. WSJ explains what the numbers mean and why they don’t tell the full story. Photo illustration: Jacob Reynolds/WSJ
HARVARD STUDY: VITAMIN D LOWERS THE RISK OF YOUNG-ONSET COLORECTAL CANCER
COMMENTARY:
Vitamin D has many beneficial effects, but my comments will be restricted to the effect of vitamin D on cancer.
Interest in this association was started by the observation that certain cancers are less common near the equator, where there is more sunlight exposure, and therefore more natural vitamin D generation in your skin.
The most information on cancer in humans Is available on colorectal, breast, prostate, and pancreatic cancer. Colorectal cancer, highlighted DWW our posting, is the only cancer that apparently is affected by vitamin D.
Several studies have suggested that vitamin D can decrease cancer cell growth, stimulate cell death, and reduce cancer blood vessel formation. Increasing cell death, or apoptosis, is what interests me the most, since this is one of the factors which increases inflammation in aging.
The infographics stated that only 300 international units of vitamin D is necessary to produce a 50 Percent reduction in cancer, and that a healthy diet generally supplies this.
I personally take 5000 international units vitamin D. This produces a blood level of about 60 ng/mL, and what the NFL recommends to keep their players healthy, and well within the maximum recommended level of 120 ng/milliliter.
Excessive vitamin D can produce an elevated calcium blood level, and mine is within normal limits. I take the higher dose because of vitamin D’s other effects, such is benefiting the immune system in a time of Conid-19.
I suggest that you get a vitamin D blood level, and also a calcium blood level if you elect to take more of this useful vitamin.
–Dr. C
Osteoporosis: Study Finds Up To 40% Greater Risk Of Hearing Loss In Women

As part of the Conservation of Hearing Study (CHEARS), researchers from Brigham and Women’s Hospital analyzed data from nearly 144,000 women who were followed for up to 34 years. They found that risk of subsequent moderate or worse hearing loss was up to 40 percent higher in study participants with osteoporosis or LBD. The study, published in the Journal of the American Geriatric Society, also found that bisphosphonates did not alter risk of hearing loss.
The researchers found that a history of vertebral fracture was associated with up to a 40 percent higher risk of hearing loss, but the same did not hold true for hip fractures, the two most common osteoporosis-related fractures. “The differing findings between these skeletal sites may reflect differences in the composition and metabolism of the bones in the spine and in the hip,” Curhan said. “These findings could provide new insight into the changes in the bone that surrounds the middle and inner ear that may contribute to hearing loss.”
HEALTHCARE: OLDER ADULTS PREFER CONVENIENCE OVER REPUTATION IN PHYSICIANS
A new study by a team from the University of Michigan Institute for Healthcare Policy and Innovation shows that adults over age 50 place more importance on convenience-related factors, rather than reputation, when choosing a doctor.
The study, based on data from IHPI’s National Poll on Healthy Aging supported by AARP and Michigan Medicine, still shows that online ratings and reviews of physicians play an important role, and should receive attention from providers and policymakers.
Dr. Jeffrey Kullgren, a U-M primary care physician and lead author of the study, describes the findings.
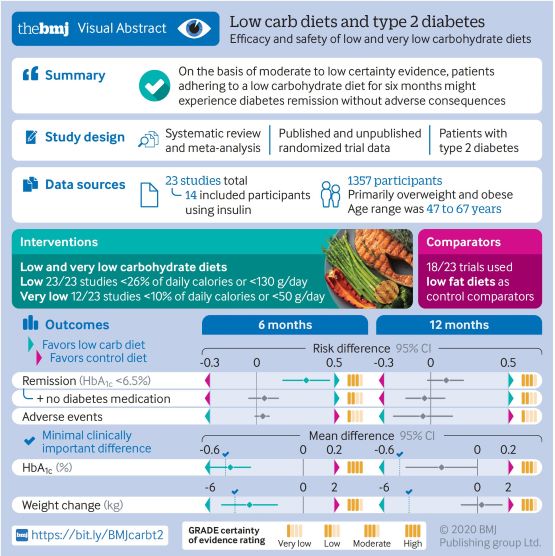
HEALTH STUDY: ‘LOW CARB DIETS’ – TYPE 2 DIABETES REMISSION IN 6 MONTHS