Statins are a type of medication used to lower the level of bad cholesterol in the blood and reduce build-up in arteries that can cause a heart attack or stroke. This short animated video explains the importance of statins, how they work, and why your doctor may prescribe them.
Category Archives: Medicine
DR. C’S MEDICINE CABINET: BENEFITS & RISKS OF ‘STATINS’
The STATIN medications are one of medicine’s greatest achievements, in my opinion. They REDUCE blood CHOLESTEROL and HEART ATTACKS in very low doses and have a good safety profile. They truly deserve to be the Best Selling class of drugs. 13 Nobel prizes have been awarded during the centuries of cholesterol research.

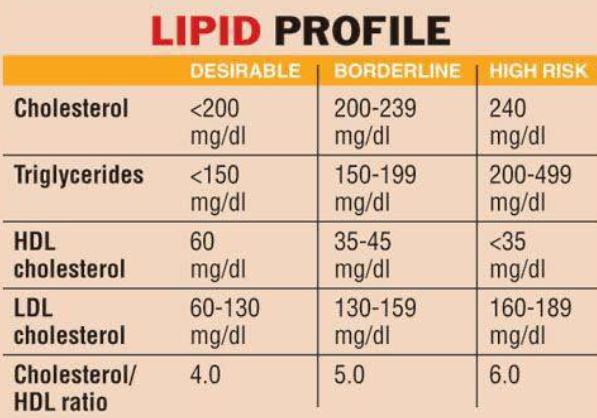
I have never had a heart attack, but do have some calcification in my Coronaries. Moreover, I have an untreated serum cholesterol level of 220 mg/dL. This is above the recommended level of 200 mg/dL, so I read up on the statins. The only concerning side effect from my viewpoint was MUSCLE PAIN.
I already have some muscle soreness from my exercise program, and did not want more, so I started at ½ of the 5 mg. dose of the statin suggested by my family doctor. This tiny dose of Rosuvastatin produced a dramatic 40 mg. Drop in my Cholesterol, and I am still hovering around the recommended level of 200 mg./dL. Instead of breaking the 5 mg. tablet in half, I now take 5 mg. every other day, since Rosuvastatin has a long half life.
One of my friends took a higher dose, and drove his cholesterol down to 100 Mg./dL. Apparently there is no serum level of cholesterol where further reduction fails to help.
Total cholesterol is divided into HDL and LDL components. My HDL, the “good” cholesterol, is thought to offset some of the cholesterol-plaque-causing effects of the LDL, or “bad” cholesterol. This makes me less than eager to raise my cholesterol and risk muscle pain.
My HIGH HDL is probably due to a combination of EXERCISE, FISH OIL and Genetics. Many of my friends “don’t tolerate” the statins, meaning that they developed muscle pain. Since they were taking the drug on faith, and not because of already-developed heart problems, they just don’t take the medication any more.
If your doctor has recommended one of the Statin drugs because of an elevated cholesterol, you might ask her to start at a lower dose. You can always work up to a higher dose if necessary. If you develop muscle pain at the higher dose, you can drop back to the dose you tolerated. Enjoy “Personalized” Medicine.
–Dr. C.
MEDICINE: ‘THREE CRITICAL BREAKTHROUGHS IN STROKE RESEARCH’ (YALE VIDEO)
Stroke is far more common than you might realize, affecting more than 795,000 people in the U.S. every year. It is a leading cause of death and long-term disability. Yet until now, treatment options have been limited, despite the prevalence and severity of stroke.
Not so long ago, doctors didn’t have much more to offer stroke victims than empathy, says Kevin Sheth, MD, Division Chief of Neurocritical Care and Emergency Neurology. “There wasn’t much you could do.” But that is changing. Recent breakthroughs offer new hope to patients and families. Beating the Clock Think of stroke as a plumbing problem in the brain. It occurs when there is a disruption of blood flow, either because of a vessel blockage (ischemic stroke) or rupture (hemorrhagic stroke).
In both cases, the interruption of blood flow starves brain cells of oxygen, causing them to become damaged and die. Delivering medical interventions early after a stroke can mean the difference between a full recovery and significant disability or death. Time matters. Unfortunately, stroke care often bottlenecks in the first stage: diagnosis. Sometimes, it’s a logistical issue; to identify the type, size, and location of a stroke requires MRI imaging, and the machinery itself can be difficult to access.
MRIs use powerful magnets to create detailed images of the body, which means they must be kept in bunker-type rooms, typically located in hospital basements. As a result, there is often a delay in getting MRI scans for stroke patients. Dr. Sheth collaborated with a group of doctors and engineers to develop a portable MRI machine. Though it captures the images doctors need to properly diagnose stroke, it uses a less powerful magnet. It is lightweight and can be easily wheeled to a patient’s bedside.
“It’s a paradigm shift – from taking a sick patient to the MRI to taking an MRI to a sick patient,” says Dr. Sheth. Stopping the Damage Once a stroke has been diagnosed, the work of mitigating the damage can begin. “Brain tissue is very vulnerable during the first hours after stroke,” says vascular neurologist Nils Petersen, MD. He and his team are using advanced neuro-monitoring technology to study how to manage a patient’s blood pressure in the very acute phase after a stroke.
Dr. Petersen’s research shows that optimal stroke treatment depends on personalization of blood pressure parameters. But calculating the ideal blood pressure for the minutes and hours after a patient has a stroke can be complicated. It depends on a variety of factors—it is not a one-size-fits-all scenario. Harnessing the Immune System Launching an inflammatory reaction is how the body responds to injury anywhere in the body – including the brain, following stroke. However, in this case, the resulting inflammation can sometimes cause even more damage.
But what if that immune response could be used to the patient’s advantage? “We’re trying to understand how we can harness the immune system’s knowledge about how to repair tissues after they’ve been injured,” says Lauren Sansing, MD, Academic Chief of the Division of Stroke and Vascular Neurology. Her team is working to understand the biological signals guiding the immune response to stroke.
That knowledge can then direct the development of targeted therapeutics for the treatment of stroke that minimize early injury and enhance recovery. “We want to be able to lead research efforts that change the lives of patients around the world,” says Dr. Sansing.
Learn about these developments and more in the video above.
For more information on aneurysms or #YaleMedicine, visit: https://www.yalemedicine.org/conditio…
HEALTH: ‘AT-HOME COVID-19 TESTS’ – ON THE WAY (VIDEO)
OraSure Technologies has blazed a trail in at-home diagnostic tests. Now, the Pennsylvania-based biotech company is working to produce a quick, over-the-counter coronavirus test that consumers can take in the privacy of their home with results available in minutes. NPR’s Allison Aubrey reports.
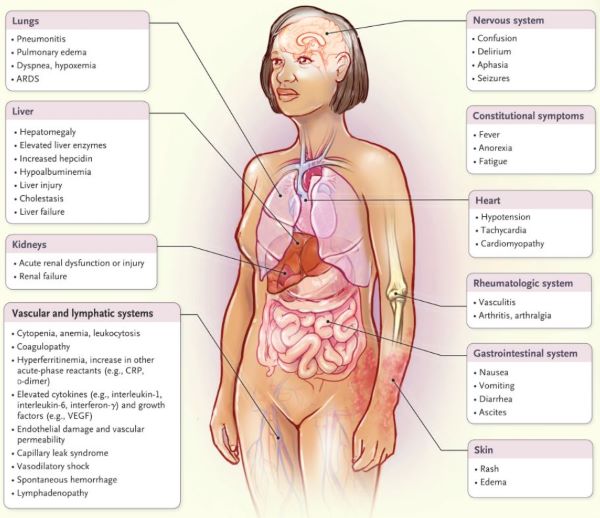
MEDICAL REVIEWS: COVID-19 & ‘CYTOKINE STORM’ (NEJM)
DR. C’S MEDICINE CABINET: Benefits & Risks Of ‘Aspirin’
Aspirin (acetylsalicylic acid) was one of the first medicines constructed, or synthesized, in a chemical laboratory. After 40 years ( medical progress wasn’t too fast in the 19th Century), Bayer investigated it as an alternative to Salicylates, which had been used since antiquity in the form of Willow bark for medical treatment, especially of FEVER and PAIN relief.
It is an understatement to say that it was successful. After almost another century, in 1982, a nobel prize was awarded for the discovery of its mode of action. Its multiplicity of effects, some of them bad, are only now becoming appreciated. My practice in medicine was in Allergic diseases, and I treated many people with nasal, sinus and asthmatic diseases.
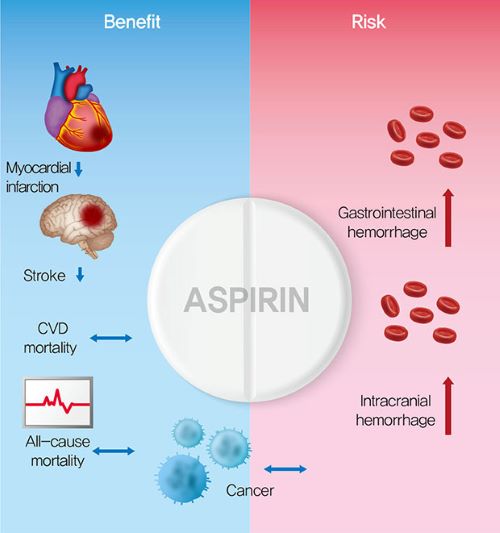
It became apparent that, in certain people, aspirin could worsen all 3 conditions, and rhinitis (with Polyps), sinusitis and asthma became known as “Samter’s Triad”, or simply ASPIRIN DISEASE. Believe it or not, the condition can be helped by “aspirin desensitization”, where the Patient was started on tiny doses of aspirin by mouth, which over a period of hours was gradually increased to a normal dose.
I would not try this at home. I sent my patients to a specialized medical center for treatment, Other undesirable effects induce bleeding disorders, stomach ulcers, and, in children, a very serious disease called Reye’s syndrome. The latter is so serious that aspirin is not often given to children; except when it is needed, such as in a condition called Kawasaki’s Disease, where it is very helpful.
I mention these details to counteract the blase attitude created by long use. No longer does the doctor say “Take an aspirin and call me in the morning”. For a long while, low-dose Aspirin was used in most Patients with coronary artery disease, as a method of preventing sudden clot formation. I took 65 mg. Of aspirin for years, even though I had no narrowing of my arteries.
Now it is found that aspirin can cause an excess of Hemorrhagic stroke, and it is not recommended in my age group and risk profile. Aspirin is a powerful medication with a wide variety of effects. Most of its beneficial effects have safer alternatives. Acetaminophen- Tylenol- is now used in place of Aspirin for Pain and fever relief. I suggest not using aspirin unless prescribed by a Doctor.
–Dr. C
MEDICINE: ‘DIABETES’ – RISKS & DIAGNOSIS (BMJ PODCAST)

In this episode of the JIM Podcast, Editor-in-Chief Richard McCallum speaks with David Cistola of Texas Tech University Health Sciences Center El Paso about American Diabetes Month.
MEDICINE: NEW ‘SMART CELL’ THERAPIES TO TREAT CANCER
Finding medicines that can kill cancer cells while leaving normal tissue unscathed is a Holy Grail of oncology research. In two new papers, scientists at UC San Francisco and Princeton University present complementary strategies to crack this problem with “smart” cell therapies—living medicines that remain inert unless triggered by combinations of proteins that only ever appear together in cancer cells.
Biological aspects of this general approach have been explored for several years in the laboratory of Wendell Lim, PhD, and colleagues in the UCSF Cell Design Initiative and National Cancer Institute– sponsored Center for Synthetic Immunology. But the new work adds a powerful new dimension to this work by combining cutting-edge therapeutic cell engineering with advanced computational methods.
For one paper, published September 23, 2020 in Cell Systems, members of Lim’s lab joined forces with the research group of computer scientist Olga G. Troyanskaya, PhD, of Princeton’s Lewis-Sigler Institute for Integrative Genomics and the Simons Foundation’s Flatiron Institute. Using a machine learning approach, the team analyzed massive databases of thousands of proteins found in both cancer and normal cells. They then combed through millions of possible protein combinations to assemble a catalog of combinations that could be used to precisely target only cancer cells while leaving normal ones alone.
In another paper, published in Science on November 27, 2020, Lim and colleagues then showed how this computationally derived protein data could be put to use to drive the design of effective and highly selective cell therapies for cancer. “Currently, most cancer treatments, including CAR T cells, are told ‘block this,’ or ‘kill this,’” said Lim, also professor and chair of cellular and molecular pharmacology and a member of the UCSF Helen Diller Family Comprehensive Cancer Center.
“We want to increase the nuance and sophistication of the decisions that a therapeutic cell makes.” Over the past decade, chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T cells have been in the spotlight as a powerful way to treat cancer.
In CAR T cell therapy, immune system cells are taken from a patient’s blood, and manipulated in the laboratory to express a specific receptor that will recognize a very particular marker, or antigen, on cancer cells. While scientists have shown that CAR T cells can be quite effective, and sometimes curative, in blood cancers such as leukemia and lymphoma, so far the method hasn’t worked well in solid tumors, such as cancers of the breast, lung, or liver.
Cells in these solid cancers often share antigens with normal cells found in other tissues, which poses the risk that CAR T cells could have off-target effects by targeting healthy organs. Also, solid tumors also often create suppressive microenvironments that limit the efficacy of CAR T cells. For Lim, cells are akin to molecular computers that can sense their environment and then integrate that information to make decisions. Since solid tumors are more complex than blood cancers, “you have to make a more complex product” to fight them, he said.
POST COVID: “THE FUTURE OF ELDERLY CARE’ (VIDEO)
Across the rich world around half of covid-19 deaths have been in care homes. Countries need to radically rethink how they care for their elderly—and some innovative solutions are on offer.
COMMENTARY:
This video has a lot of information that would be of help to anyone who has a spouse or parent who is aging, especially if their frailty includes dementia. There were several good, general points.
As hard as it is to get old, it is even harder to be a caretaker of someone whose aging includes memory loss. Hired caretakers burn out at a high rate. The video highlighted Indonesia as a location that is compassionate, and gives quality care at about half the cost in developed countries.
The percentage of the elderly population needing care may well be 50% in 2050. I would not have guessed it, but the video asserts that 50% of individuals over 65 years of age need some help.
It is much better to stay at home, and medical sensor technology is making this increasingly possible. AI would be able to detect changes in a person’s routine that could be flagged.
Of course, it is much better to stay healthy longer. My posting “growing old” addresses this.
–Dr. C.
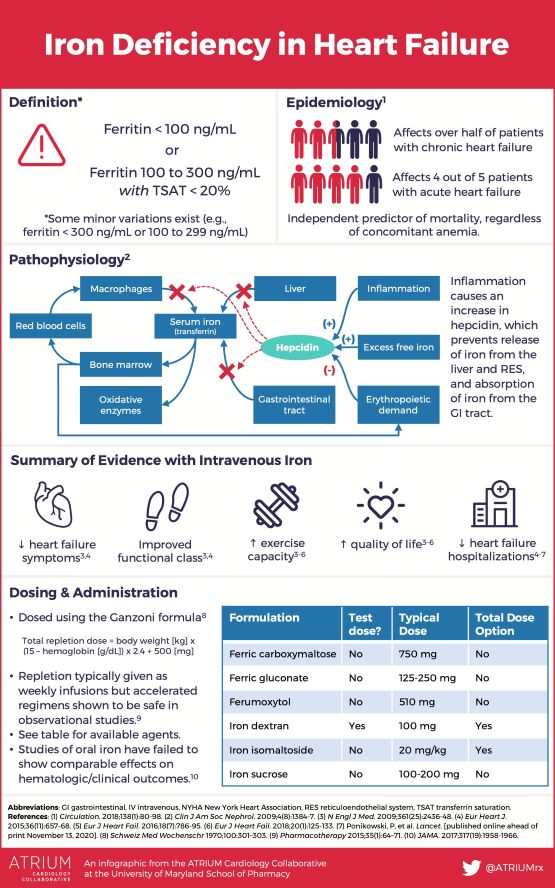
DR. C’S MEDICINE CABINET: THE BENEFITS OF “IRON”
Iron is the most common element, by weight, on earth, so it should come as no surprise that it has evolved to be an essential component in the mechanism that is life.
The ENERGY of the eukaryotic cell is dependent on the Iron in mitochondria, which are elaborate electron-transfer mechanisms. To quote Nobel Laureate Albert Szent Gyorgyi, “Life is nothing but an electron looking for a place of rest”.
Iron is essential, so it is possible to have too little of it. There is no physiologic pathway to get rid of it and so you can have too much iron in your body, which comprises a disease called Hemochromatosis. Excessive Iron can be TOXIC to the body, and produce damaging free radicals.
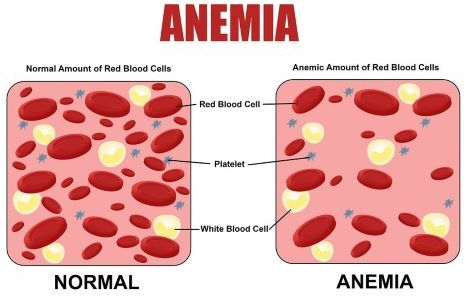
Deficiency of iron will produce ANEMIA. Regulation of incoming Iron is the body’s way of keeping excessive Iron out. It is absorbed only in the upper part of the small intestine, and a special protein called Hepcidin can block it from release into the circulation. It is carried through the blood by Transferrin and also Ferritin, which stores the iron that is not in the hemoglobin of RED BLOOD CELLS, the main storehouse of iron.
Blood loss is a common problem which leads to increased Iron requirement, This is reflected in the increase in RDA of Iron in Women during their menstruating years. Colonic Cancer, among other conditions, can also bleed and lead to the anemia of Iron deficiency. This is the reason for Doctors ordering a test for “occult”, or hidden, blood in the stools. My reason for taking Iron is a continuing loss of blood from the small intestine.
I have had multiple colonoscopies and Gastroenteroscopies to rule out cancer and other blood-losing conditions in the lower and upper intestinal tract. The small intestine is the “silent” area to gastroenterologists, and I cannot have the Capsule/camera examination because of my small bowel surgery.
I must take extra iron, and hope that this will be sufficient to keep me from developing anemia again. Green vegetables and red meat are more satisfactory sources, but insufficient for me. I worry a little about the recent finding that Heart Failure has been associated with Ferritin levels below 100 ng./ml.
I struggle to keep mine at 50 ng. by taking 2 tablets of feosol daily and dealIng with the subsequent constipation. An ANNUAL PHYSICAL and laboratory examination is important for the maintenance of health. Enough Iron and blood are important factors for vigorous Well-being. —
–Dr. C.
INFOGRAPHIC: