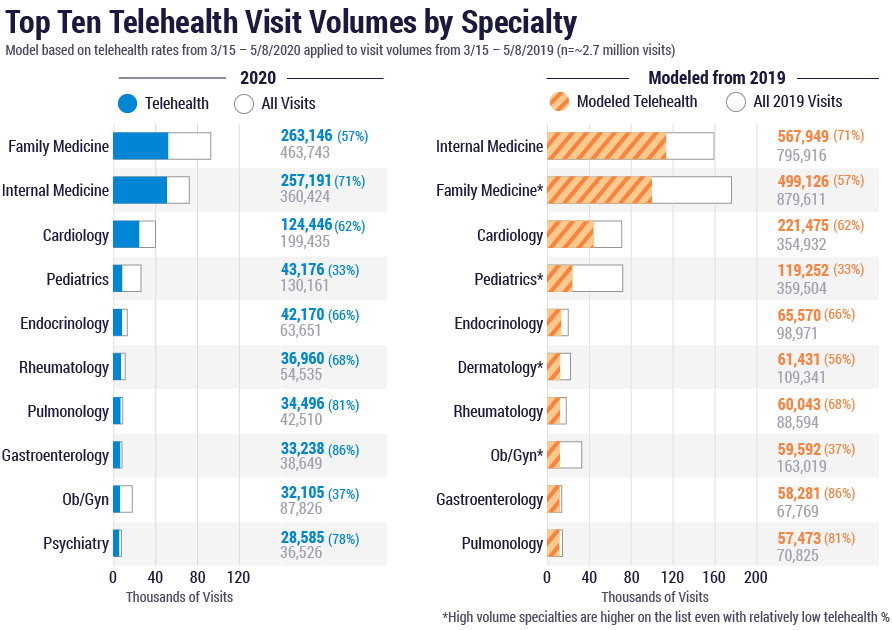
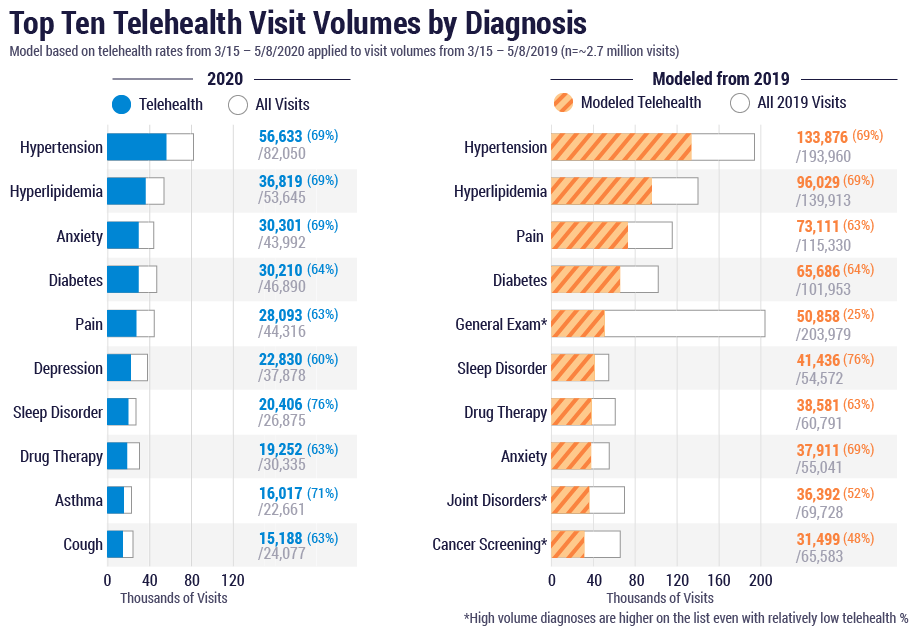


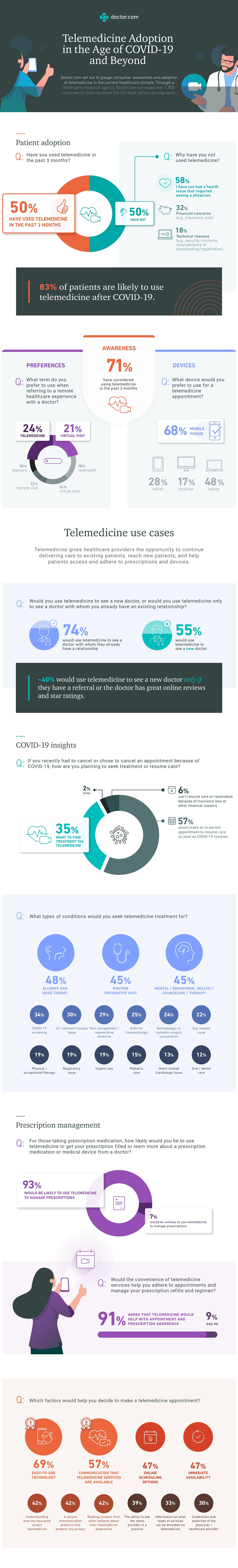
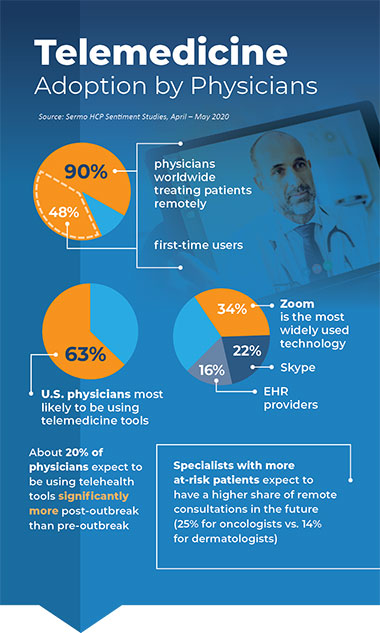
Diagnostics World (June 30, 2020): The shift from face-to-face patient visits to remote medical appointments is a worldwide phenomenon, but most especially in the U.S., finds a recent global survey conducted by the doctors-only social networking platform Sermo. Unsurprisingly, Zoom tops the list of most-mentioned technologies. About one-fifth of surveyed doctors say they expect to be using telehealth tools “significantly” more post-pandemic than before COVID-19 upended business as usual.
From ‘Government Technology’ (June 29, 2020):
The hospital system — the first in the country — wired bedside video cameras and microphones on a secure network in 2000 so a medical team could monitor patients at multiple hospitals’ intensive care units from one command center around the clock.

When Sentara Healthcare first launched its “eICU,” the plan was to provide an extra set of eyes on critical patients, especially overnight when staffing was down to a skeleton crew.
Before the coronavirus arrived in Virginia, the average number of telemedicine visits within Sentara Medical Group was about 20 a day. Now, it is more than 2,000 a day, according to the company. Between March and June 21, its clinicians had 314,000 total patient visits, with about 51 percent of them happening virtually.
COMMENTARY
Telemedicine has been slowly developing for 10 or 20 years. The models have been developing according to the requirements of their local areas.
Dartmouth deals with a rural area and has sophisticated aid to it’s associated hospitals and transportation systems to bring Stabilized patients to the main hospital.
Sentara deals with a more urban area and has a central brain aiding the peripheral hospitals in the delivery of treatment locally.
The Tele intensive care unit system of Santara features a central ” Mission Control” With patients in multiple peripheral Intensive care units connected by telemetry. This efficient system allows the peripheral ICUs to operate at a higher level with less staff.
Such telemetry could allow convalescent hospitals and even nursing homes to improve medical care.
With such excellent models one can hope that American medicine will rapidly improve in the post Covid era, riding the wave of telehealth advances.
From Penn Medicine (June 24, 2020):
After surveying almost 800 gastroenterology and hepatology patients and their physicians at Penn Medicine, 67 percent of both viewed their video and telephone appointments held during the peak of the COVID-19 pandemic as positive and acceptable substitutes to in-person appointments.

From March 16 to April 10, 2020, 94 percent of gastroenterology and hepatology appointments at Penn Medicine were performed using telemedicine in order to mitigate risks of COVID-19 spread while continuing to advance care as patients self-isolated at home. A telemedicine visit meant either a video visit (similar to FaceTime or Skype) or one via phone in which clinicians largely performed routine and non-urgent care.

On a Friday afternoon last summer, a patient, “Barb,” texted me: “Call me. I can’t breathe.” As a heart failure nurse serving rural patients, getting messages like Barb’s launches my adrenaline. I called her immediately.
A month earlier, I’d trained Barb to send daily vital signs via my clinic’s digital portal—blood pressure, weight, heart rate, and oxygen saturation.
Barb was suffering from a congestive heart failure exacerbation: her lungs were filling with fluid. If we didn’t remove it, she’d need to be hospitalized or worse.
Once I was sure she wasn’t in emergency distress, I called the clinic’s cardiologist for instructions. Then I phoned Barb’s pharmacy and ordered a new diuretic to add to her regimen—a water pill so powerful in its fluid off-loading effect that I’ve nicknamed it the Bellagio. Within two hours, Barb had taken the pill and begun to urinate out the fluid flooding her lungs. By the next morning, she was breathing comfortably.
Without access to a telehealth program, Barb would probably have gone to the emergency room, then to the intensive care unit for expensive intravenous medications.
Our Dartmouth-Hitchcock TeleHealth Service Lines include the following:
Outpatient Virtual Visits connect patients and health care providers to Dartmouth-Hitchcock specialists via scheduled outpatient TeleHealth visits. Outpatient Virtual Visits increase access to specialty care services for patients located in rural or underserved areas and improves the patient experience via more convenient access to specialty care with reduced travel. D-H Outpatient Virtual Visit services currently offered including specialty clinic appointments, direct-to-patient home visits and inpatient consultations.
TeleEmergencyprovides a board-certified emergency medicine physician and an experienced emergency nurse to join the bedside team, on-demand, 24/7. Using high-quality, two-way audio-video communication, the TeleEmergency team assists by whatever means requested, including nursing documentation, direct patient care, consultation, a second set of eyes, assistance with transfer coordination, acceptance, and/or transport.
TeleICN allows D-H Neonatologists to join your bedside team to serve the needs of you and your patients for a wide variety of diagnoses. Some babies require a higher level of care as they adjust to life outside of the mother’s body. The 24/7 support of ICN services helps keep patients and families closer to home by supporting clinical decision making and providing expert evaluations and recommendations. If a transfer is necessary, our specialized ICN team will assist in transporting that patient.
TeleICU provides experienced intensive care physicians and critical care nurses to augment, not replace, the bedside team. In addition, the service provides behind-the-scenes, high-level monitoring and sophisticated analytical algorithms to identifying concerning trends prior to patient deterioration. Not only does this result in decreased mortality and length of stay; it also allows more patients to get their ICU care close to home.
TeleNeurologyprovides board-certified neurologists on-demand 24/7 for Emergency Department and inpatient consultations. This includes not only stroke (including evaluation and recommendations, and assistance with tPA administration), but also assistance with other adult neurologic emergencies. This allows a lower cost coverage option for hospitals with limited or no neurologist access, improved tPA administration rates and decreased transfers.
TelePharmacyconnects hospitals to a team of dedicated pharmacists who can provide medication order review and processing as well as clinical consultation, allowing hospitals to optimize their internal staffing while remaining compliant with order review regulations. D-H TelePharmacy improves medication efficacy, patient safety and staff satisfaction while also supporting the integration of pharmacy delivery within hospital systems and/or regions, including protocols and order sets.
TelePsychiatryenables prompt assessment and management of patients in the Emergency Department or inpatient setting for locations that do not have around-the-clock psychiatric coverage. Board-certified psychiatrists provide 24/7, on-demand assessments including expedited admit vs. discharge decisions, early management recommendations, and assistance with medication management, while improving the ultimate patient trajectory.
TeleUrgent Care provides back-up, support and consultation to Urgent Care providers by emergency medicine physicians via high-definition, two-way audio-video conferencing. TeleUrgent Care physician input can include general recommendations, real-time patient assessments, second opinions, advice regarding the need and timing of additional emergent or urgent evaluations, review of radiographic images, and assistance with volume surges.
From MD+DI (June 17, 2020):

Remote-care solutions like telehealth and wearable devices are included in the new approach that healthcare professionals will be embracing as they position their businesses to best serve patients in a COVID-19 world. Digital healthcare product solutions address critical issues for the remote delivery of care or the “hospital at home” that have been resonating long before we began looking at all our interactions through a social-distancing lens.
Wearables and On-Body Devices – Real-time data collection and communication are critical to digital health initiatives. More than half of survey respondents—52%—said they are currently developing or planning to develop wearable or on-body devices as part of their strategy. Another 33% said the same for patient-monitoring solutions.

Miniaturization, flexible circuitry, and biometric capturing sensors are leading to exciting new devices that will help patients in recovery or with chronic issues. The data communicated from these solutions will equip healthcare providers and patients with the data that can transform healthcare.
Seamless technology integration – A range of emerging technologies, including artificial intelligence (AI), 5G, cloud-based applications, and a growing roster of IoMT devices.
More than nine in 10 healthcare solution providers agree that the collection and purposing of data should be standardized to enable interoperability between devices and within product platforms, according to the survey.
H4D facilitates access to healthcare by allowing patients to consult a doctor remotely in the Consult Station®, the first connected local telemedicine booth. This medical device allows quality healthcare to be delivered for primary care, occupational health, and general health promotion.
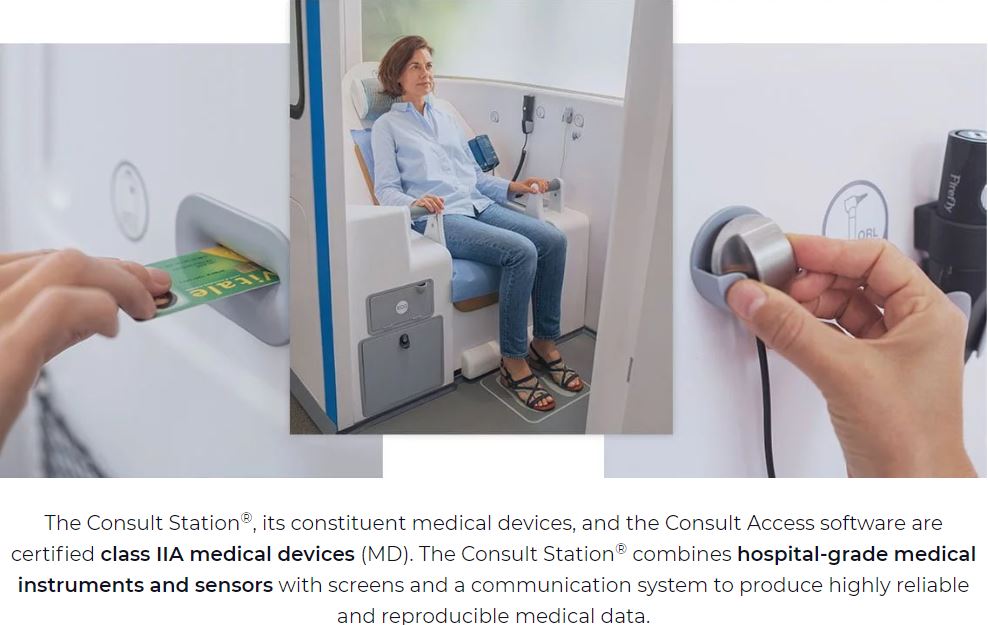
COMMENTARY
CONVENIENCE, SIMPLICITY, and SAFETY area all goals of TECHNOLOGY going forward.
The “hands-free” check-in for hospitals and hotels are convenient and safety, but require a certain level of familiarity with technology, and may be Hard for the elderly to use. I think about the airport check-in kiosks, and store check-out points. The solution is to have “helpers” stationed by to assist.
The Telemedicine booth, with devices for examination of the ears, nose, and throat, a stethoscope probe for the lungs, payment port, video camera, etc certainly offers convenience, but may need helpers for guidance, and to clean after every use.
I’m betting on a super I Phone in all areas, although cost and band width improvement will be needed.