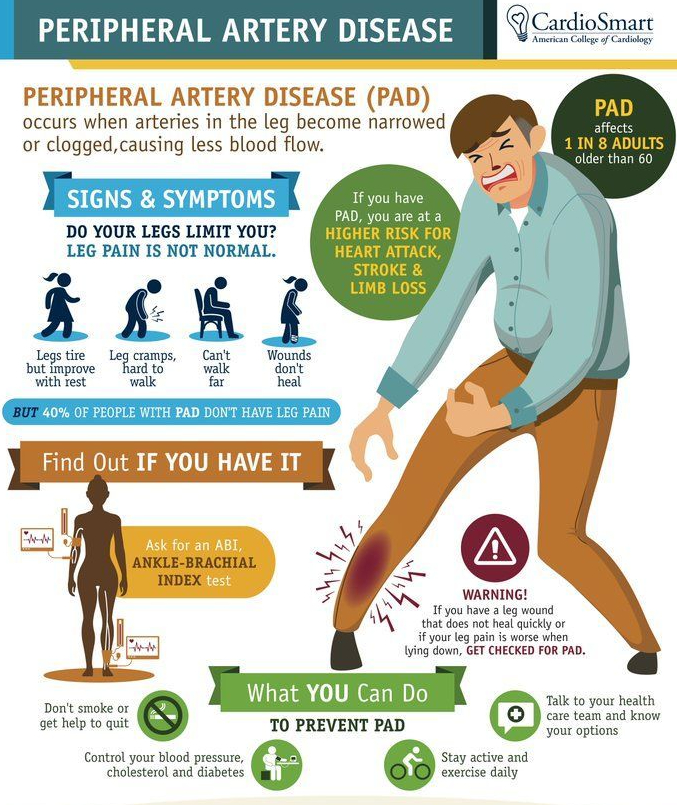
Coronary artery bypass graft (CABG) was supported as superior to fractional flow reserve (FFR)–guided percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) for three-vessel coronary artery disease (CAD). PCI failed to meet noninferiority criteria at 1-year follow-up in a study comparing outcomes between FFR-guided PCI using contemporary stents and CABG. This adds to existing evidence showing superior outcomes with CABG in patients with the most-complex CAD.
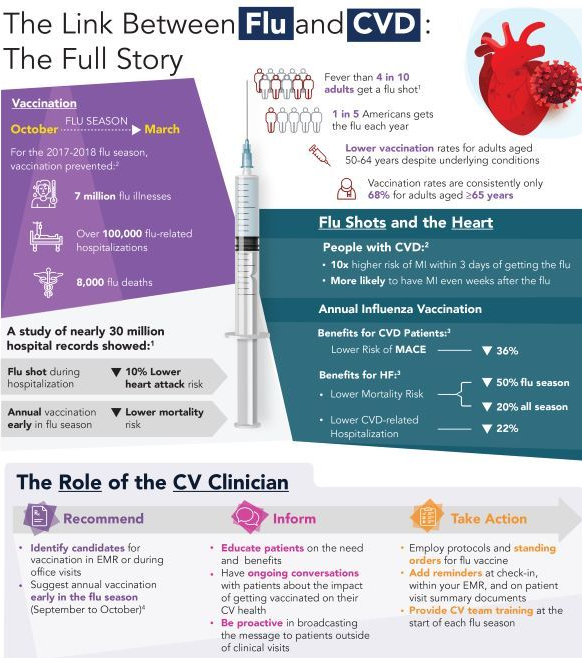
The sodium–glucose transporter-2 (SGLT-2) inhibitor empagliflozin was found to be beneficial in heart failure with preserved ejection fraction. Empagliflozin is the first medication shown to improve outcomes in this population. It’s unknown if this is a class effect of all SGLT-2 inhibitors, but this could be a game changer.
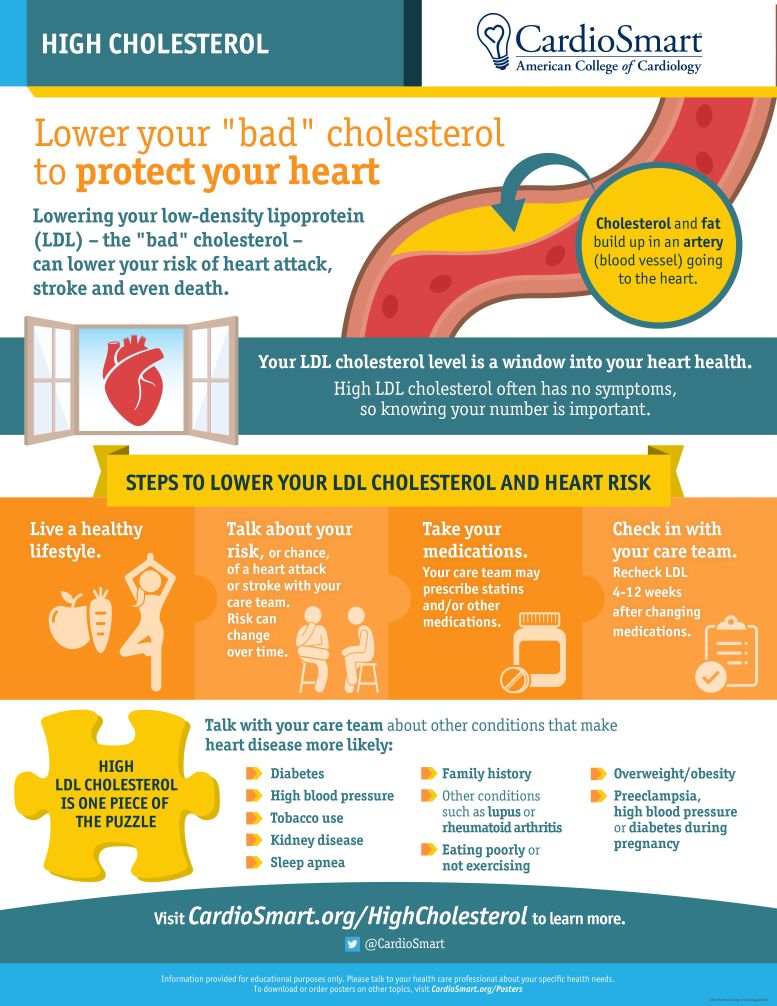
Poor-quality carbohydrates were linked to cardiovascular mortality, around the world. Consumption of higher-glycemic-index carbohydrates was associated with higher rates of cardiovascular disease and mortality in countries all around the world. These data are particularly important because lower-income countries often have diets high in refined carbohydrates, which may worsen cardiovascular disparities.
New guidelines for managing valvular heart disease were released. These new guidelines add or elevate several recommendations for transcatheter therapy, and they lower thresholds for intervention in some conditions.
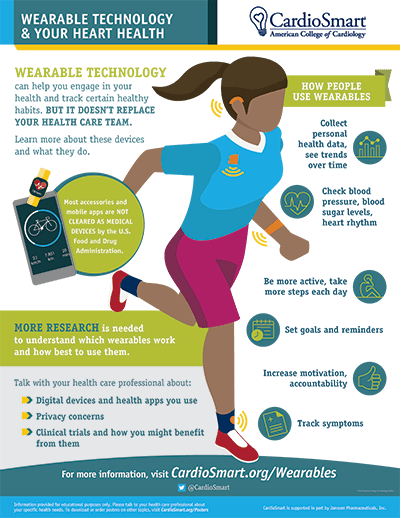
The editors of Circulation: Cardiovascular Quality and Outcomes addressed racial-ethnic disparities. The editors affirmed that structural racism is a public health crisis and that the scientific publishing community can play a role in addressing it.
Tricuspid annuloplasty for moderate regurgitation during mitral-valve surgery was of unclear benefit. Annuloplasty was associated with less progression of moderate tricuspid regurgitation but more pacemakers at 2 years. Unfortunately, this mixed outcome does not clearly inform the decision on performing annuloplasty at the time of surgery, and longer-term follow-up is needed.
Immediate angiography was not beneficial in out-of-hospital cardiac arrest without ST elevation. Patients with out-of-hospital cardiac arrest who did not have ST elevation on their initial ECG did not benefit from immediate angiography. Although a potential coronary culprit was identified in about 40% of patients, neurologic injury was by far the most frequent cause of death, negating any benefit from coronary revascularization.
Many statin side effects are related to the “nocebo” effect. A creative study enrolled 60 people with statin intolerance and gave them 12 randomly ordered 1-month treatment periods: 4 periods of no medication, 4 of placebo, and 4 of statin. Symptom intensity did not differ between placebo and statin periods and, interestingly, some even had more symptoms on placebo. This demonstrates that some cases of “statin intolerance” may be related to the “nocebo” effect.
Shorter duration of dual antiplatelet therapy following PCI/stent placement was found to be acceptable in patients with high bleeding risk. A large, randomized trial found that 1 month of dual antiplatelet therapy provided similar clinical outcomes and a lower bleeding risk than 3-to-6-month regimens for this challenging patient subset.
“De-escalation” of dual antiplatelet therapy for patients undergoing PCI for acute myocardial infarction (MI). This industry-funded study evaluated patients who had received 1 month of aspirin plus ticagrelor after acute MI and stent placement and “de-escalated” half to aspirin plus clopidogrel. At 1 year, there was significantly less bleeding in the de-escalation group and a nonsignificant trend toward fewer ischemic events as well.