




Our skin is home to billions of microorganisms, the vast majority of which are bacteria. Much like the microbiome in our gut, these microbes play a crucial part in keeping us healthy. They are part of a finely balanced ecosystem of friendly or ‘commensal’ bacteria, which protect our skin by creating an inhospitable environment for would-be invaders, bolstering the physical integrity of the skin, and training the immune system to distinguish commensal inhabitants from pathogens. A number of skin conditions are now understood to be influenced by a breakdown of this microbial ecosystem. Researchers are working out whether restoring the balance can treat these conditions. Understanding the ecology of this rich community is likely to be an important part of both dermatology and the study of the microbiome. Read more in https://www.nature.com/collections/sk…
Screening testing is one tool the University of Pennsylvania is using to help reduce the risk of COVID-19 spread within the University community. That’s why we’re performing saliva-based viral testing for students, faculty, postdocs, and staff who are on campus.

Stroke is far more common than you might realize, affecting more than 795,000 people in the U.S. every year. It is a leading cause of death and long-term disability. Yet until now, treatment options have been limited, despite the prevalence and severity of stroke.
Not so long ago, doctors didn’t have much more to offer stroke victims than empathy, says Kevin Sheth, MD, Division Chief of Neurocritical Care and Emergency Neurology. “There wasn’t much you could do.” But that is changing. Recent breakthroughs offer new hope to patients and families. Beating the Clock Think of stroke as a plumbing problem in the brain. It occurs when there is a disruption of blood flow, either because of a vessel blockage (ischemic stroke) or rupture (hemorrhagic stroke).
In both cases, the interruption of blood flow starves brain cells of oxygen, causing them to become damaged and die. Delivering medical interventions early after a stroke can mean the difference between a full recovery and significant disability or death. Time matters. Unfortunately, stroke care often bottlenecks in the first stage: diagnosis. Sometimes, it’s a logistical issue; to identify the type, size, and location of a stroke requires MRI imaging, and the machinery itself can be difficult to access.
MRIs use powerful magnets to create detailed images of the body, which means they must be kept in bunker-type rooms, typically located in hospital basements. As a result, there is often a delay in getting MRI scans for stroke patients. Dr. Sheth collaborated with a group of doctors and engineers to develop a portable MRI machine. Though it captures the images doctors need to properly diagnose stroke, it uses a less powerful magnet. It is lightweight and can be easily wheeled to a patient’s bedside.
“It’s a paradigm shift – from taking a sick patient to the MRI to taking an MRI to a sick patient,” says Dr. Sheth. Stopping the Damage Once a stroke has been diagnosed, the work of mitigating the damage can begin. “Brain tissue is very vulnerable during the first hours after stroke,” says vascular neurologist Nils Petersen, MD. He and his team are using advanced neuro-monitoring technology to study how to manage a patient’s blood pressure in the very acute phase after a stroke.
Dr. Petersen’s research shows that optimal stroke treatment depends on personalization of blood pressure parameters. But calculating the ideal blood pressure for the minutes and hours after a patient has a stroke can be complicated. It depends on a variety of factors—it is not a one-size-fits-all scenario. Harnessing the Immune System Launching an inflammatory reaction is how the body responds to injury anywhere in the body – including the brain, following stroke. However, in this case, the resulting inflammation can sometimes cause even more damage.
But what if that immune response could be used to the patient’s advantage? “We’re trying to understand how we can harness the immune system’s knowledge about how to repair tissues after they’ve been injured,” says Lauren Sansing, MD, Academic Chief of the Division of Stroke and Vascular Neurology. Her team is working to understand the biological signals guiding the immune response to stroke.
That knowledge can then direct the development of targeted therapeutics for the treatment of stroke that minimize early injury and enhance recovery. “We want to be able to lead research efforts that change the lives of patients around the world,” says Dr. Sansing.
Learn about these developments and more in the video above.
For more information on aneurysms or #YaleMedicine, visit: https://www.yalemedicine.org/conditio…
OraSure Technologies has blazed a trail in at-home diagnostic tests. Now, the Pennsylvania-based biotech company is working to produce a quick, over-the-counter coronavirus test that consumers can take in the privacy of their home with results available in minutes. NPR’s Allison Aubrey reports.
DELIRIUM is a rapidly-developing TEMPORARY DEMENTIA in response to almost any trauma, infection or stress, usually in a hospital setting, with its restrictive, isolating and disorienting environment.
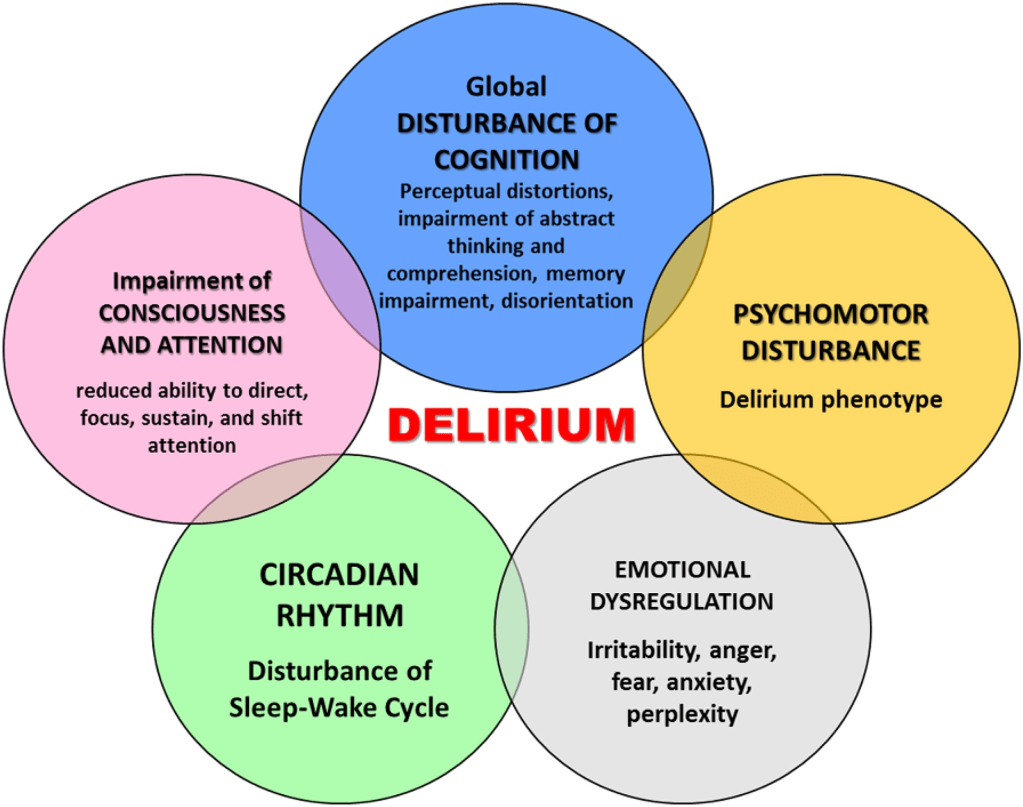
I had little appreciation of the frequency or economic hazard of Delirium before I encountered this infographic. I knew little about the causative mechanisms, and after reading about it, I still don’t know what is going on. But I do know one thing; I don’t want to become delirious and risk its ominous outcome. To improve my odds, I want to keep myself as healthy as possible.
To prevent loss of focus, cognition and memory, challenge the Brain as much as possible. To prevent or restrain infection, support the immune system with a healthy diet. To combat sleep disturbances, practice Sleep Hygiene. To maintain adequate oxygen and nutrient delivery to the Brain, support a healthy cardiovascular-pulmonary system with regular aerobic exercise.
These preventative steps will also postpone the FRAILTY on which delirium feeds. This fuzziness, which afflicts most conditions with PSYCHIATRIC OVERTONES, should not be surprising, since the human Brain, the location of Delirium, is the most complex entity in the known universe.
Medical Knowledge of Delirium is still at the descriptive stage, even though it has been a feature of human life since Ancient times. Causation? Excess or Deficiency of most neurotransmitters have been described. To paraphrase “cytokine storm”, which can incidentally cause Delirium, one could call the condition a “neurotransmitter storm”.
Treatment? If the Delirious Patient is on a Psychotropic medication, try stopping it. If not taking such medication, try starting it. The only universal green light is Good general supportive care with IV fluids, oxygen, nutrition, and psychological support, with gentle, regular attention. Please read the accompanying Mayo Clinic article for a more conventional discussion.