“The data we analyzed suggested a nearly threefold reduction in revision surgery in patients who received bone marrow aspirate concentrate, compared to those who did not,” says Bradley Schoch, M.D., an orthopedic surgeon and principal investigator. “This procedure is growing in use throughout the practice of orthopedic surgery and commonly added as a surgical adjunct to rotator cuff tears.”
Mayo Clinic – Applying regenerative medicine to a common shoulder surgery could have an impact on the need for follow-up revision surgery in some patients, according to a Mayo Clinic study of real-world evidence.
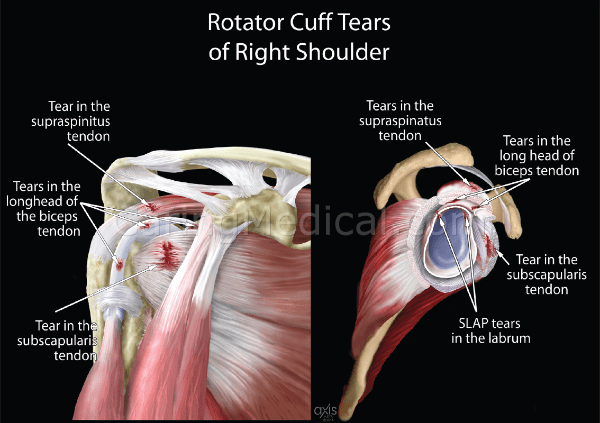
Mayo Clinic researchers analyzed the largest set of data available to determine if adding bone marrow aspirate concentrate to repaired tissue after standard rotator cuff surgery would improve outcomes for patients. Bone marrow aspirate is fluid taken from a patient’s bone marrow that contains concentrated growth factors, stem cells and other specialized cells that may regenerate tissue and cartilage.
The analysis identified 760 patients who had a regenerative intervention added to augment rotator cuff repair surgery. Those patients were compared to 3,888 patients who did not have any biologic intervention at the time of surgery. The data indicated that 114 patients who opted for bone marrow aspirate concentrate at the time of surgery were less likely to need a second surgery.
The results of the Mayo Clinic study are published in the Orthopaedic Journal of Sports Medicine.



