A weekly podcast on the latest medical, science and telehealth news.
Category Archives: Medicine
Medical Update: A Review Of Tuberculosis In 2023
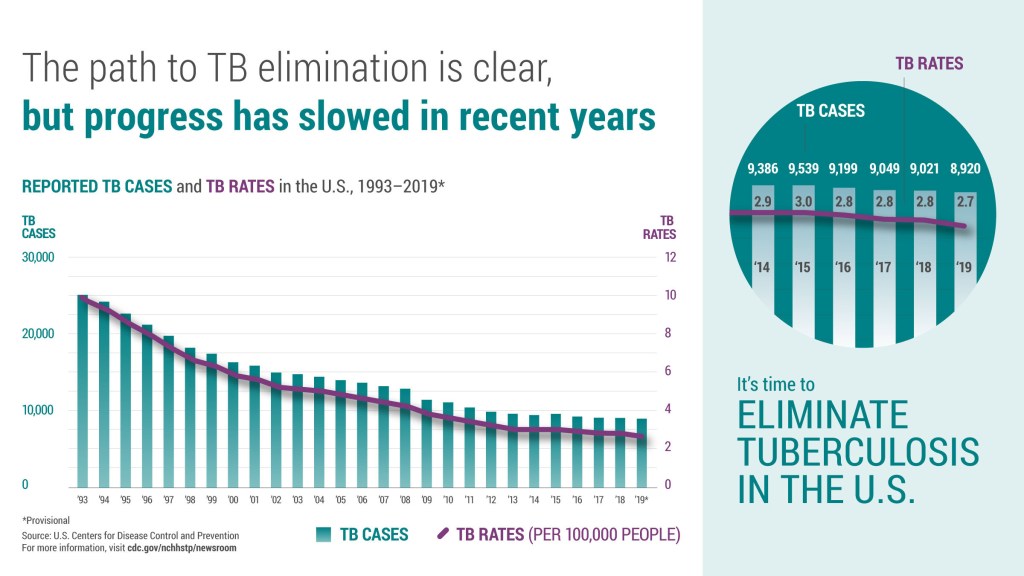
TB has been a gradually diminishing presence in the United States for decades, and currently there are only 2.4 cases per hundred thousand people in our country.
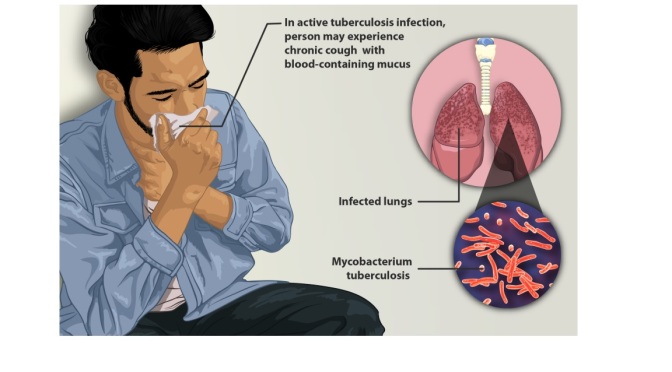
When I was in medical school, TB was still a big problem, and we learned about the fever, night sweats, weight loss and coughing up blood from active tuberculosis. With any of these symptoms, you should, of course, check with a physician.
These severe infections still happen but, currently, tuberculosis occurs primarily in immigrants from other countries, homeless people, prison inmates, people with Immune deficiency, such as cancel therapy and HIV infection.
TB is also more common in Asians, Native Americans and Eskimos, and Hispanics.
The Ordinary middle class American citizen these days is unlikely to catch tuberculosis, unless they are exposed to somebody that has an active, open case, more likely in people described above.
On first contact, the Tubercle bacillus is almost always controlled by the immune system. Most of these primary cases are without symptoms, and after a few weeks could be picked up by an immune blood test, called the T-spot.TB, or the skin tuberculin test. The chest x-ray can also show a spot on the lung with primary tuberculosis. it is with reactivation that the severe symptoms of secondary TB, described above, can occur.
My own inclination would be to get tested with exposure to any of the groups mentioned above, especially if they have a cough.
Incidentally, there was a dip in tuberculosis incidence during the contagion versus COVID-19 pandemic, showing one more advantage in avoiding big, inside groups.
Catching tuberculosis at the earliest possible moment still continues to be important, especially since long drawn out disease in individuals who have defective immune systems has led to the development of drug resistant organisms.
—Dr. C.
Reviews: Brain Tumor Risk Factors & Symptoms
Mayo Clinic (May 17, 2023) – Learning about a brain tumor can be intimidating. Alyx Porter, M.D., a neuro-oncologist at Mayo Clinic, walks you through the facts, the questions, and the answers to help you better understand this condition.
Video timeline: 0:00 Introduction 0:37 What is a brain tumor? 1:38 Who gets a brain tumor? / Risk factors 2:26 Symptoms of a brain tumor 3:36 How is a brain tumor diagnosed? 4:13 Treatment options 6:24 Coping methods/ What now? 7:14 Ending
For more reading visit: https://mayocl.in/3ciMNB7.
Heart Health: What To Know About Cholesterol
May 16, 2023: Patients have many questions about how to lower cholesterol and what to do after a high cholesterol diagnosis.
Dr. Ashish Sarraju answers some of these common questions including why fasting before your test is important, what all of the different tests tell your doctor and what you can do to help your heart.
Infographic: Systemic Arterial Hypertension

Systemic arterial hypertension is the most important modifiable risk factor for all-cause morbidity and mortality worldwide and is associated with an increased risk of cardiovascular disease (CVD).
Fewer than half of those with hypertension are aware of their condition, and many others are aware but not treated or inadequately treated, although successful treatment of hypertension reduces the global burden of disease and mortality. The aetiology of hypertension involves the complex interplay of environmental and pathophysiological factors that affect multiple systems, as well as genetic predisposition.
The evaluation of patients with hypertension includes accurate standardized blood pressure (BP) measurement, assessment of the patients’ predicted risk of atherosclerotic CVD and evidence of target-organ damage, and detection of secondary causes of hypertension and presence of comorbidities (such as CVD and kidney disease). Lifestyle changes, including dietary modifications and increased physical activity, are effective in lowering BP and preventing hypertension and its CVD sequelae.
Pharmacological therapy is very effective in lowering BP and in preventing CVD outcomes in most patients; first-line antihypertensive medications include angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors, angiotensin II receptor blockers, dihydropyridine calcium-channel blockers and thiazide diuretics.
Heart Disease: A Surgeon’s View Of Aorta Surgery
Cleveland Clinic (MAY 9, 2023): Have you ever wondered what your surgeon thinks about when they are deciding if you need an operation?
Dr. Lars Svensson and Dr. Marijan Koprivanac discuss all things aorta, such as your past medical history, current health, and how your surgeon looks to the future to provide the best options for you.
DOCTORS PODCAST: MEDICAL & TELEHEALTH NEWS (May 07)
A weekly podcast on the latest medical, science and telehealth news.
HEALTH: HOW THE PANDEMIC RESHAPED AMERICAN LIFE
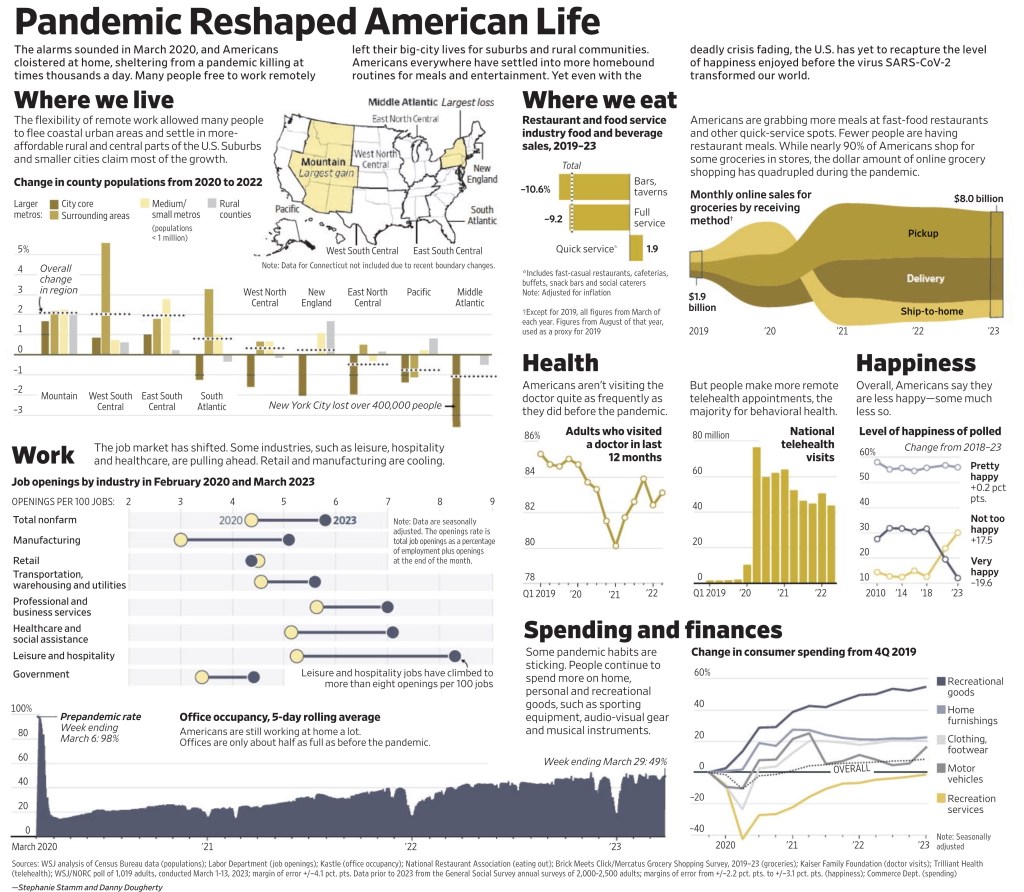
Wall Street Journal (May 5, 2023) – The alarms sounded in March 2020, and Americans cloistered at home, sheltering from a pandemic killing at times thousands a day. Many people free to work remotely left their big-city lives for suburbs and rural communities. Americans everywhere have settled into more homebound routines for meals and entertainment. Yet even with the deadly crisis fading, the U.S. has yet to recapture the level of happiness enjoyed before the virus SARS-CoV-2 transformed our world.
Insomnia: Can Cognitive Behavioral Therapy Help?
May 4, 2023: Difficulty initiating and maintaining sleep is a common problem for many patients. Over-the-counter sleeping aids are used by many and we commonly get asked for prescription medications to help with their sleep.
Unfortunately, the ideal sleeping medication doesn’t exist and many have potentially worrisome adverse effects, some produce daytime somnolence and others may have the potential to produce dependence.
Cognitive behavioral therapy is an alternative treatment option to pharmacologic therapy and is safe, can be easily taught, and offers an alternative to the many with chronic insomnia. In this podcast, we’ll discuss this innovative treatment option with sleep expert, Michael H. Silber, M.B.Ch.B., a neurologist at the Mayo Clinic.
Bacteria: Helicobacter Pylori Infection Review
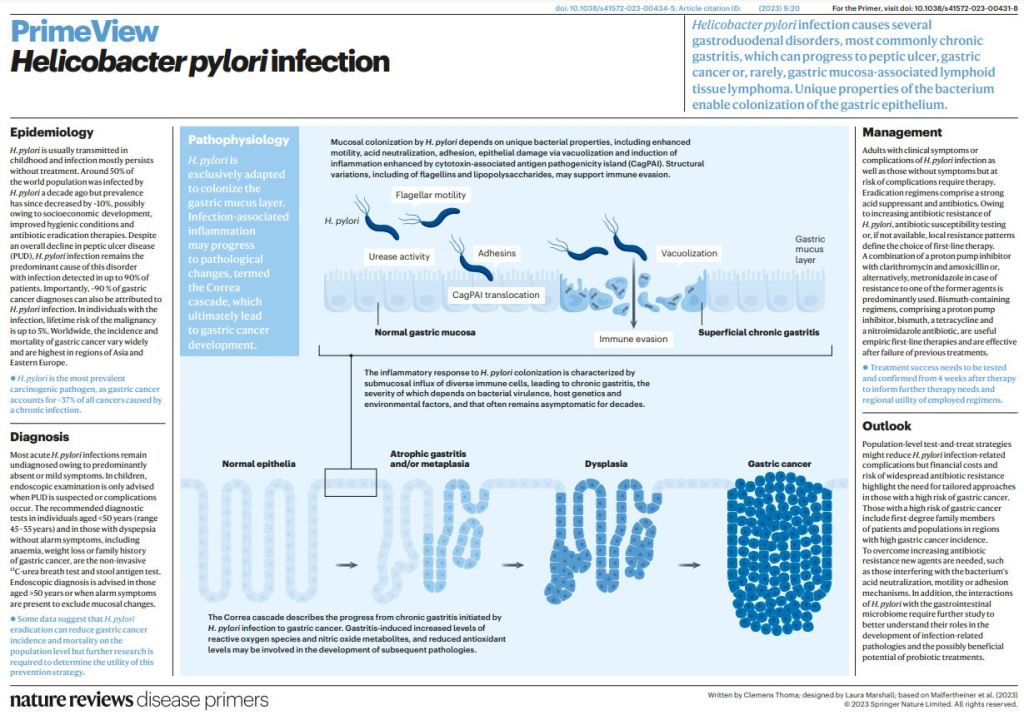
Helicobacter pylori infection causes chronic gastritis, which can progress to severe gastroduodenal pathologies, including peptic ulcer, gastric cancer and gastric mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue lymphoma. H. pylori is usually transmitted in childhood and persists for life if untreated. The infection affects around half of the population in the world but prevalence varies according to location and sanitation standards. H. pylori has unique properties to colonize gastric epithelium in an acidic environment.
The pathophysiology of H. pylori infection is dependent on complex bacterial virulence mechanisms and their interaction with the host immune system and environmental factors, resulting in distinct gastritis phenotypes that determine possible progression to different gastroduodenal pathologies. The causative role of H. pylori infection in gastric cancer development presents the opportunity for preventive screen-and-treat strategies. Invasive, endoscopy-based and non-invasive methods, including breath, stool and serological tests, are used in the diagnosis of H. pylori infection.
Their use depends on the specific individual patient history and local availability. H. pylori treatment consists of a strong acid suppressant in various combinations with antibiotics and/or bismuth. The dramatic increase in resistance to key antibiotics used in H. pylori eradication demands antibiotic susceptibility testing, surveillance of resistance and antibiotic stewardship.