Mayo Clinic (April 20, 2023) – Fitness training balances five elements of good health. Your overall exercise plan should include aerobic fitness, strength training, core exercises, balance training, and flexibility and stretching.
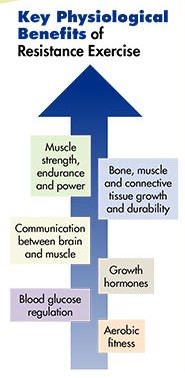
- Exercise controls weight.
Exercise can help control your weight, prevent excess weight gain or maintain weight loss. When you take part in physical activity, you burn calories. The more intense the activity, the more calories you burn. - Exercise combats heart conditions and diseases.
Being active boosts high-density lipoprotein, or HDL or “good,” cholesterol, and it decreases unhealthy triglycerides. This one-two punch keeps your blood flowing smoothly, which decreases your risk of cardiovascular diseases. - Exercise improves mood.
Physical activity stimulates various brain chemicals that may leave you feeling happier, more relaxed and less anxious. You also may feel better about your appearance when you exercise regularly, which can boost your confidence and improve your self-esteem. - Exercise boosts energy.
Regular physical activity can improve your muscle strength and boost your endurance. Exercise delivers oxygen and nutrients to your tissues and helps your cardiovascular system work more efficiently. And when your heart and lung health improve, you have more energy to tackle daily chores. - Exercise promotes better sleep.
Regular physical activity can help you fall asleep faster, get better sleep and deepen your sleep. - Exercise puts the spark back into your sex life.
Regular physical activity can improve energy levels and increase your confidence about your physical appearance, which may boost your sex life. Regular physical activity may enhance arousal for women, and men who exercise regularly are less likely to have problems with erectile dysfunction than men who don’t exercise. - Exercise can be fun and social.
Exercise and physical activity can be enjoyable. Exercise gives you a chance to unwind, enjoy the outdoors or simply take part in activities that make you happy. Physical activity also can help you connect with family or friends in a fun social setting.