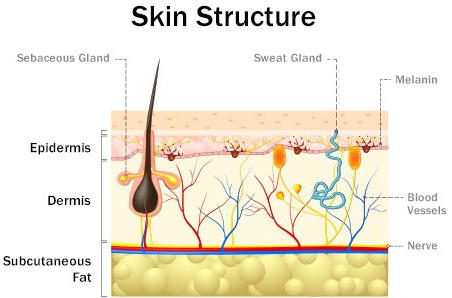
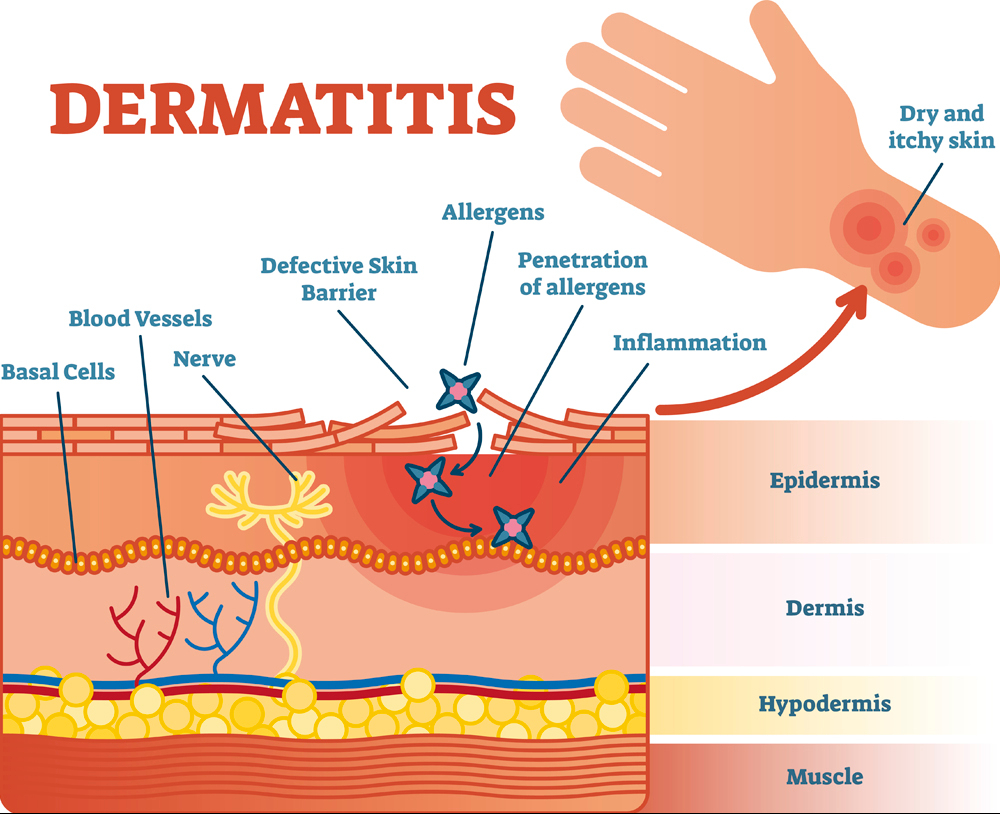
Our Kidneys and Liver have a lot in common. They are not dramatic, take-care-of-me-now organs like our Hearts and Brain, but usually do their job quietly until they lose almost all of their function. They have lots of reserve; you can donate one of your kidneys or a piece of your liver and notice no change. They are both vital organs, and you will die without them.
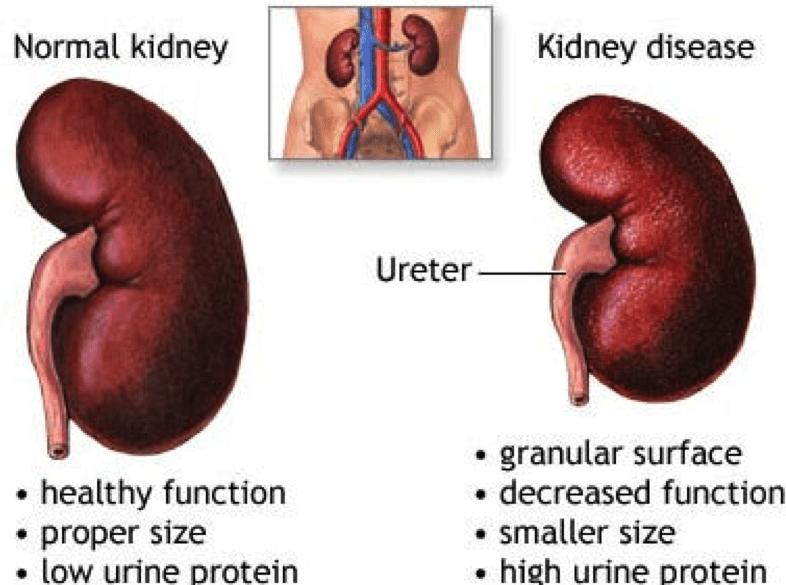
Since they both help clear wastes and toxins from the bloodstream and produce hormones, they SHARE SYMPTOMS such as nausea, vomiting, fatigue, and mental changes.Their performance can be checked by blood tests. Healthy habits will protect their -and your- survival.
Certain Drugs impair their operation. They are both composed of many identical functional units, the nephron in the kidney, and the hepatic lobule in the liver.
The GLOMERULUS of the Nephron is a tuft or ball of capillaries and associated kidney cells that allow the fluid and dissolved molecules of the blood to come through, while restraining the larger proteins and cells of the blood, keeping them in the vascular system. The smaller molecules of sodium, potassium, urea and other waste products leak through the glomerulus.
This filtered liquid travels through the long, folded kidney tubules, where the RIGHT AMOUNT of salt and water are REABSORBED. This keeps the vascular fluids, the internal environment, the MILIEU INTERIOR, perfectly well adjusted for proper cell function. It is when the chemical environment of the body falls out of adjustment, when the kidneys FAIL to do their job, that the cells of the body cannot function properly, and Symptoms-fatigue, lethargy etc. – develop.
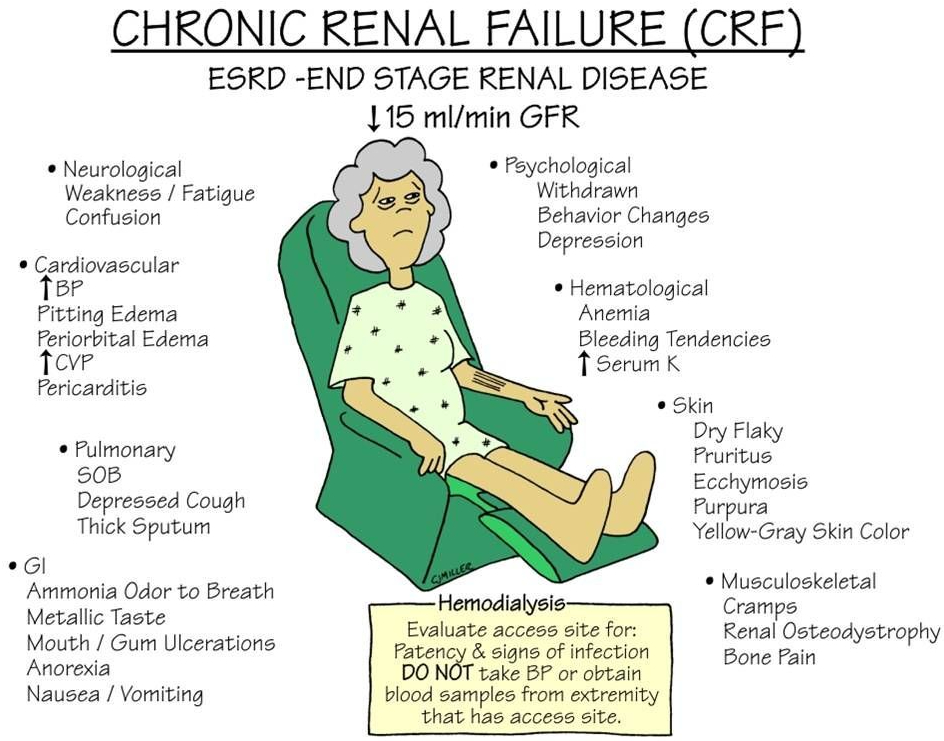
BLOOD PRESSURE is intimately involved with the KIDNEYS, which has an Endocrine function. The Renin( Renal=kidneys) Angiotensin system is a major regulator of blood pressure.
You may have heard of the ACE-2 receptor as the binding site of th COVID Virus. This Angiotensin Converting Enzyme receptor is on the surface of cells all over the body and normally functions to control blood pressure.
DIABETES is the most common cause of end stage renal disease (ESRD), bringing our healthy triad of SLEEP DIET and EXERCISE to our attention once again.
POLYCYSTIC KIDNEY DISEASE is an inherited condition where many nephrons fail to hook up to the urine collecting system, and the fluid builds up into cysts, which then eventually replace the rest of the kidney. Pressure from urine blockage by an enlarged prostate, or even lack of ureteral valves can also back up into the kidneys and eventually cause ESRD.
Infections and autoimmune diseases can result in ESRD. Treatment of ESRD is usually a Kidney transplant or Dialysis. There is a waiting list for the former and the latter is life-altering. You can’t beat a healthy lifestyle.