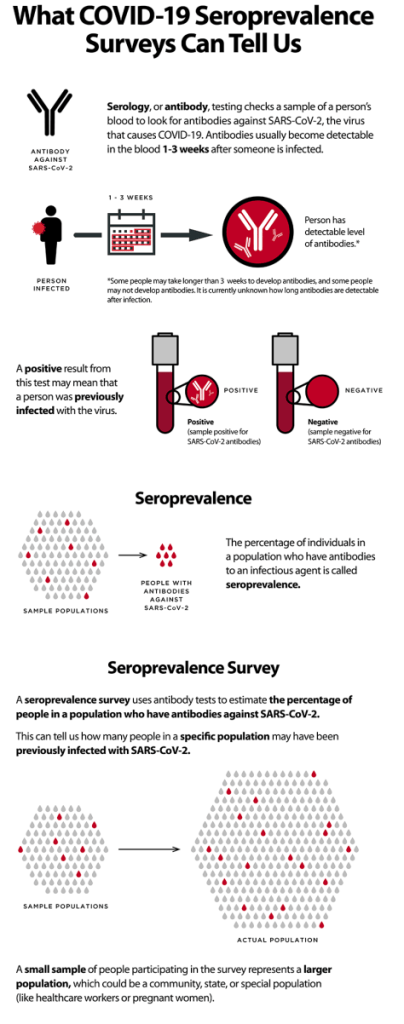
INFOGRAPHIC: “COVID-19 ANTIBODY TESTING” (CDC)


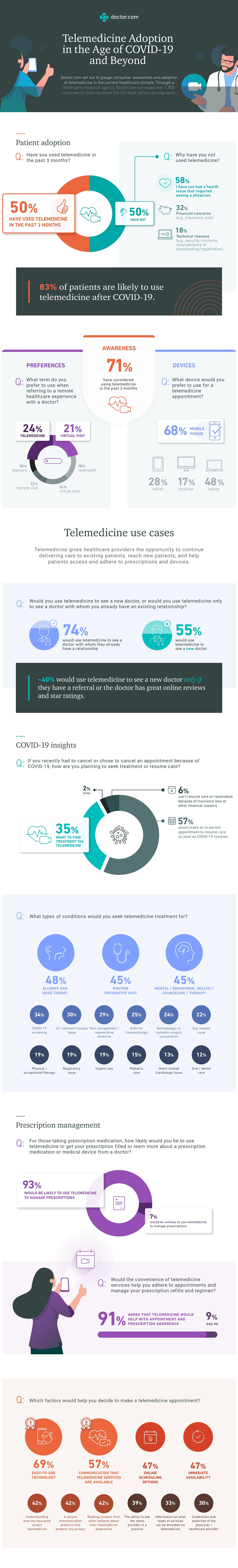

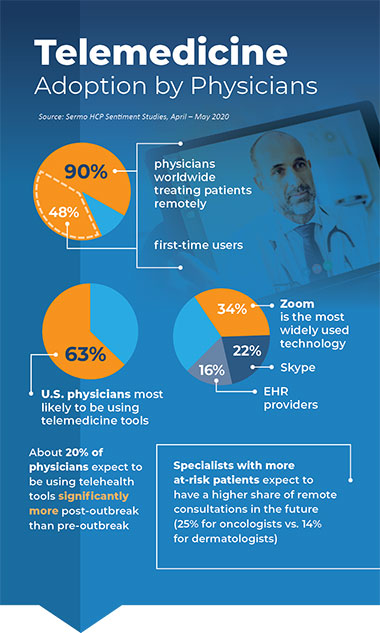
Diagnostics World (June 30, 2020): The shift from face-to-face patient visits to remote medical appointments is a worldwide phenomenon, but most especially in the U.S., finds a recent global survey conducted by the doctors-only social networking platform Sermo. Unsurprisingly, Zoom tops the list of most-mentioned technologies. About one-fifth of surveyed doctors say they expect to be using telehealth tools “significantly” more post-pandemic than before COVID-19 upended business as usual.
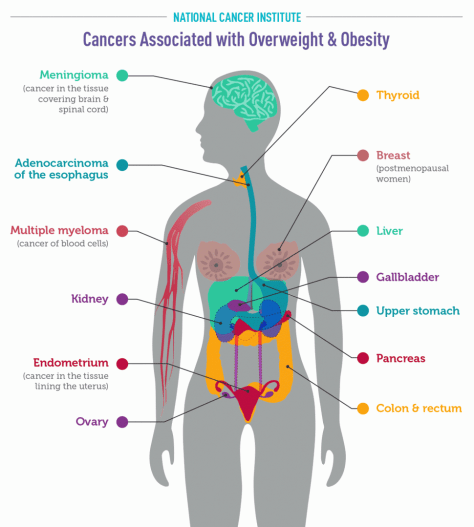
There is consistent evidence that higher amounts of body fat are associated with increased risks of a number of cancers (6), including:
COMMENTARY
Obesity increases the incidence of cancer, and complicates its treatment.
A healthy life style.,’including good sleep, diet and exercise, should prevent obesity in all but extreme genetic aberrations.
It is better to prevent problems than to grapple with them.
Stay healthy!


COMMENTARY
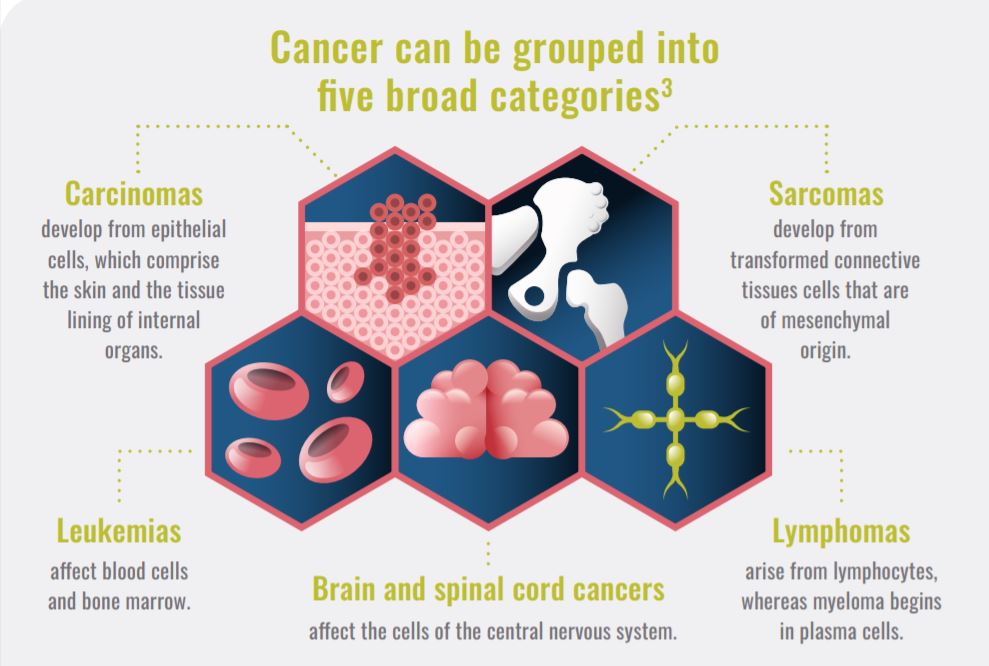
This infographic is a high-level discussion of cancer, with plenty of information to keep a Physicians’ interest.
The Human Body is a complex Community of individual cells that normally work together with admirable Harmony. Each individual cell is supplied with all its’ wants, and vigorously does its’ part for the Body.
Occasionally a ROGUE CELL escapes constraints and GOES ITS’ OWN WAY.
This has been happening from the beginning of multicellular life, and these MISCREANTS have EVOLVED to preserve themselves and have an amazing bag of TRICKS.
They are Very resourceful just like VIRUSES, which can also cause CANCER.
These twin threats give modern medical technology about all it can handle, and more.
PREVENTATIVE care offers a remedy.
Prevention is not at all complex, but of course requires thought, energy and planning. Prevention is difficult to square up with the easy, effortless, intuitive life we yearn for.
Do you have the resolve to give SLEEP, DIET and EXERCISE a chance?

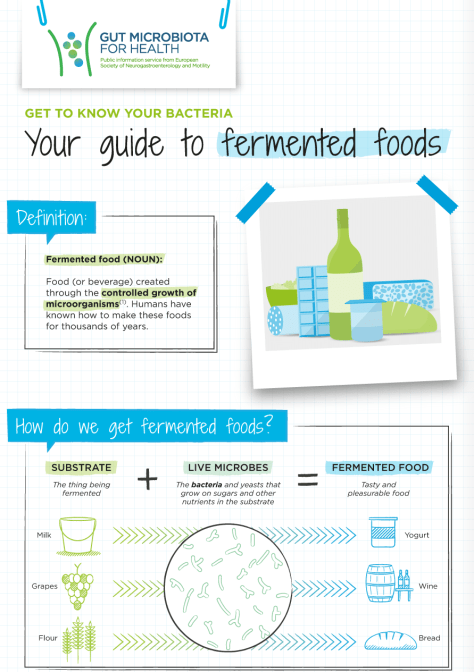
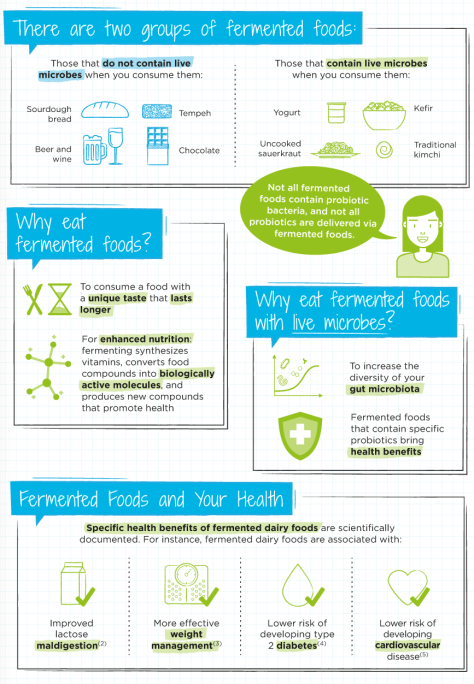
This article gave an interesting classification of fermented foods, pointing out that with some, like bread and wine, we eat the products of fermentation without the living organisms, while with others like kefir and yogurt, we eat the viable critters also.
Lactobacilli are called probiotics, and are supposed to have health benefits. It is not proven that they do, but at least the lactobacilli use up some of the sugar we would otherwise be eating, and taste good.
The problem with the claim that they diversify and benefit our microbiome, and crowd out the bad germs, is that they do not generally attach to our intestinal walls, and go right through with the rest of our food. They don’t stick around long enough to do any good.
My late wife had a bad infection with a bad actor called Clostridium difficile, which caused her to have a severe, bloody enterocolitis. After the second hospitalization with this affliction, an Infectious disease doctor suggested “culturelle”, which contained a patented Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG, which WAS supposedly proven to attach for a while. My wife took this, and never had another attack.
I still take this daily, “on faith”. Gullible me. Fecal transplants are now used effectively for C. Dif. enterocolitis. Avoiding unnecessary antibiotics, which wipe out your normal microbiome, your “good guy competition”, is An even better idea, but seems risky.
BOTTOM LINE: Kefir and yogurt are calorie depleted, and taste good. What is not to like?