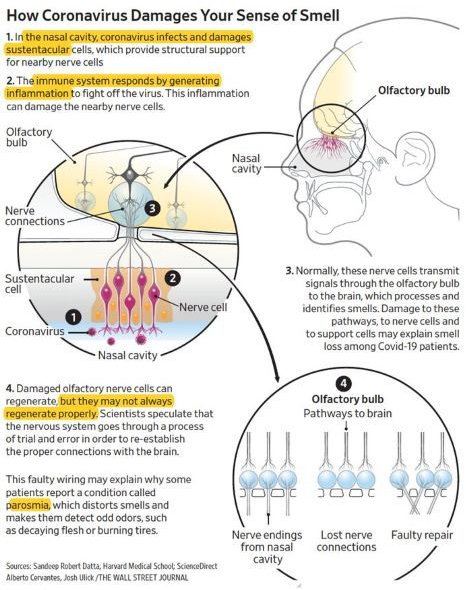
Tag Archives: Health Infographics
HEALTH: ‘BLOOD PRESSURE – KNOW YOUR NUMBERS’

INFOGRAPHIC: EXERCISE FOR ‘CLAUDICATION’ (BMJ STUDY)
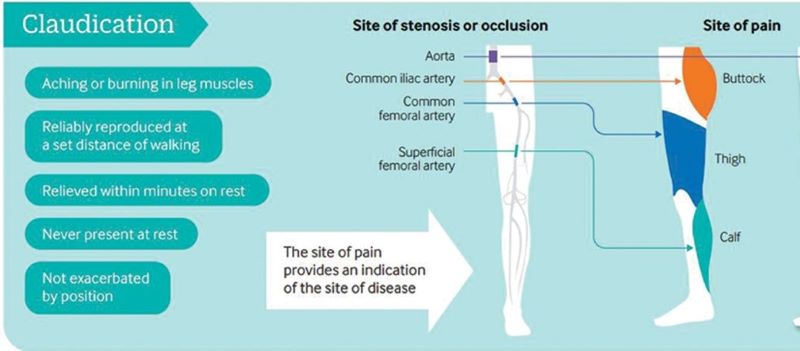
Exercise training is a safe, effective and low-cost intervention for improving walking ability in patients with IC. Additional benefits may include improvements in QoL, muscle strength and cardiorespiratory fitness. Clinical guidelines advocate supervised exercise training as a primary therapy for IC, with walking as the primary modality.
However, evidence is emerging for the role of various other modes of exercise including cycling and progressive resistance training to supplement walking training. In addition, there is emerging evidence for home-based exercise programmes. Revascularisation or drug treatment options should only be considered in patients if exercise training provides insufficient symptomatic relief.
Abstract
Peripheral artery disease (PAD) is caused by atherosclerotic narrowing of the arteries supplying the lower limbs often resulting in intermittent claudication, evident as pain or cramping while walking. Supervised exercise training elicits clinically meaningful benefits in walking ability and quality of life. Walking is the modality of exercise with the strongest evidence and is recommended in several national and international guidelines. Alternate forms of exercise such as upper- or lower-body cycling may be used, if required by certain patients, although there is less evidence for these types of programmes. The evidence for progressive resistance training is growing and patients can also engage in strength-based training alongside a walking programme. For those unable to attend a supervised class (strongest evidence), home-based or ‘self-facilitated’ exercise programmes are known to improve walking distance when compared to simple advice. All exercise programmes, independent of the mode of delivery, should be progressive and individually prescribed where possible, considering disease severity, comorbidities and initial exercise capacity. All patients should aim to accumulate at least 30 min of aerobic activity, at least three times a week, for at least 3 months, ideally in the form of walking exercise to near-maximal claudication pain.
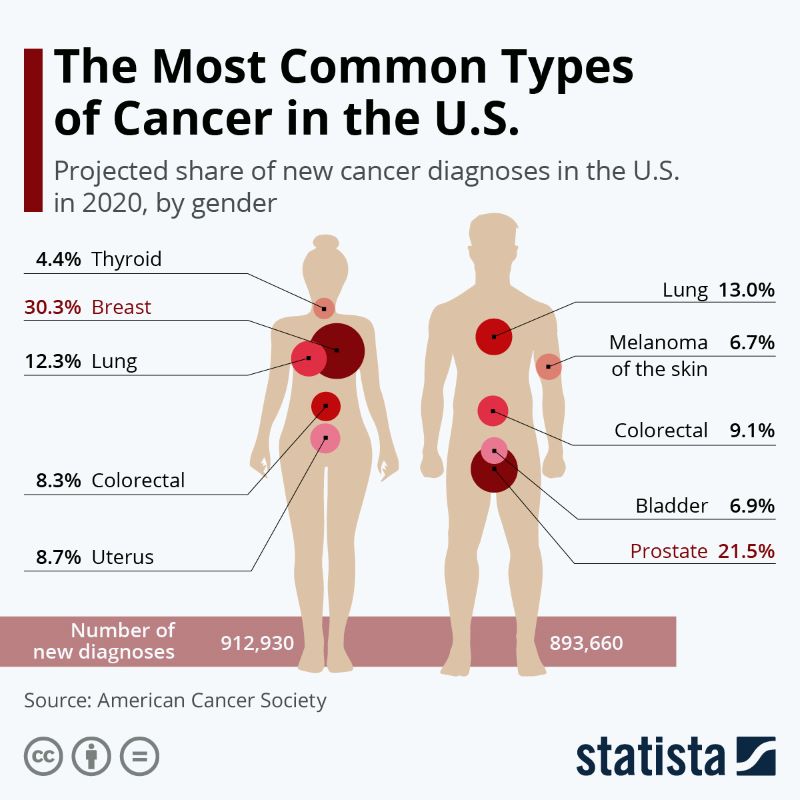
Infographic: ‘The Most Common Types Of Cancer’
STUDY: “ANTI-INFLAMATORY” DIET OF VEGETABLES, FRUITS, COFFEE & TEA LOWERS HEART DISEASE AND STROKE RISKS
Dietary patterns with a higher proinflammatory potential were associated with higher CVD risk. Reducing the inflammatory potential of the diet may potentially provide an effective strategy for CVD prevention.
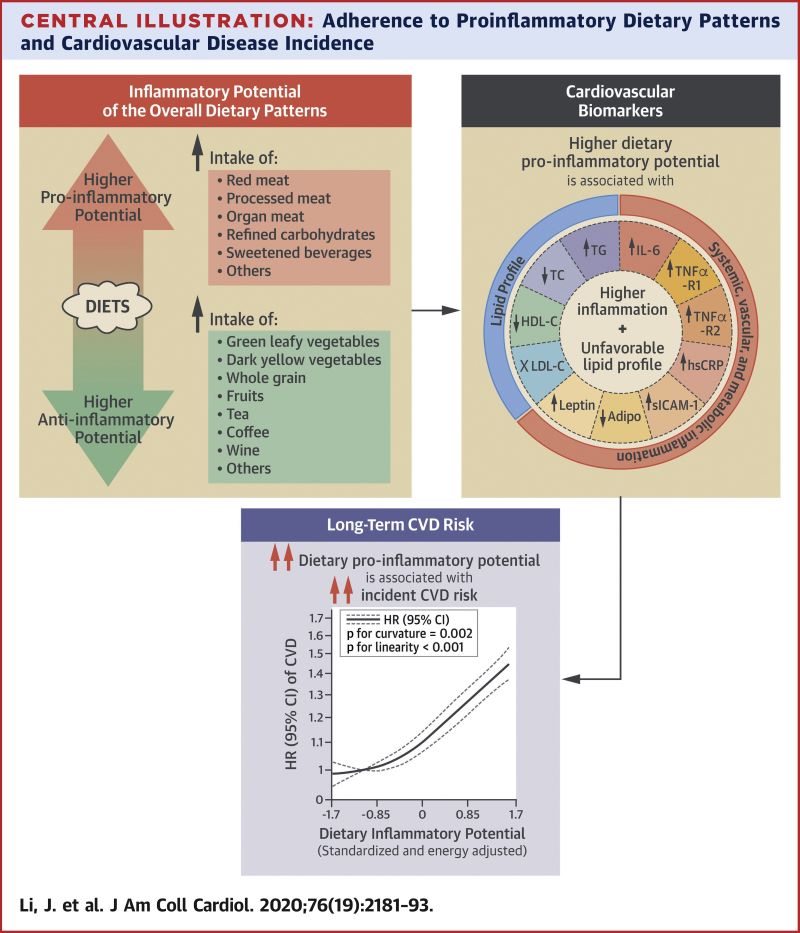
Background
Inflammation plays an important role in cardiovascular disease (CVD) development. Diet modulates inflammation; however, it remains unknown whether dietary patterns with higher inflammatory potential are associated with long-term CVD risk.
INFOGRAPHIC: ‘DIFFERENCES BETWEEN COVID-19, THE FLU AND ALLERGIES (2020)
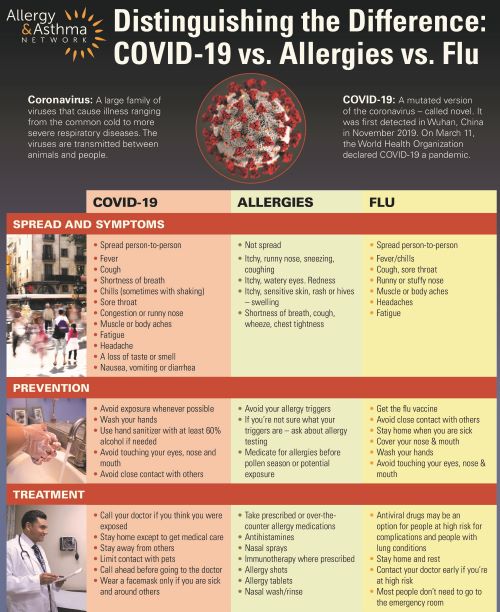

COMMENTARY:
The infographic by the allergy and asthma foundation aims to distinguish between Covid, Influenza and allergy. I would like to discuss more than symptoms. Covid and Influenza are both caused by invading infectious viruses.
Allergy is an over-response by the sensitized body to harmless proteins from the environment Covid and Influenza viruses cause direct damage to the lining membranes of the respiratory tract provoking a protective response by the body which produces inflammation in the nose and lung. Rhinitis, bronchitis and pneumonia result, depending on the site of the inflammation.
The symptoms of Allergy are far different from both Influenza and covid. ITCHING of the nose, eyes and skin is the hallmark of allergic Rhinitis, allergic conjunctivitis and Hives, respectively. Influenza or Covid Infection of the nose, eyes and airways can produce sneezing, redness, coughing and difficulty breathing, but not usually itching.
Fever is characteristic of Influenza and Covid, but not of uncomplicated Allergy. Asthma can result from either infection or allergy, but is a separate beast, caused by release of different inflammatory cytokines.
The ASTHMATIC REACTION shows itself in the BLOCKAGE of breathing of air OUT of the lung, on EXHALATION. This blockage on exhalation in asthma is heard as wheezing, a musical sound. Just ask the wheezing person to take a deep breath IN, which should be easier, and then breathe out as fast as possible, which should be slower and more difficult. Fever is not a feature of uncomplicated Asthma. Influenza and Covid.
Both produce FEVER, fatigue, aching and usually coughing. Covid has the greater linkage with Coughing, which often progresses to Shortness of breath. Both Influenza and Covid can produce a sore throat and runny nose. LOSS OF SENSE OF SMELL is unique to Covid, although if your nose is stuffy, the sense of smell can be impaired. Influenza preys on the very young, which are generally spared from Covid.
If you are careful about social distancing and wear masks in public, and get sick, Covid is more likely, since COVID IS MORE CONTAGIOUS THAN INFLUENZA. Covid protections will probably result in fewer cases of Influenza this winter.
To summarize,both the “flu” and Covid 19 are infectious conditions, vastly different from allergy, which is a derailed body defense mechanism. Any of the three can result in an asthmatic reaction, though the fever of influenza often lessens the Asthmatic response to that condition.. Covid is much more contagious and severe than influenza and can cause more widespread organ damage. Be sure to practice MASK WEARING AND SOCIAL DISTANCING.
If you have asthma and it worsens, in my opinion, this favors covid. My asthmatic patients often got better with the fever of Influenza. If you have a CHILD that gets sick, it is more likely to be Influenza than Covid.
–Dr. C
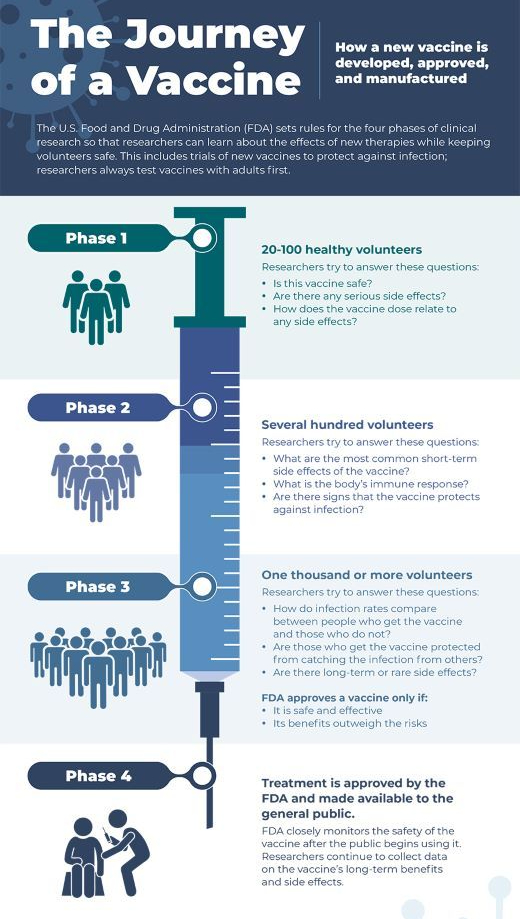
COVID-19 INFOGRAPHIC: ‘THE JOURNEY OF A VACCINE’ (NIH)

HEALTH: ‘DIABETES AND CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE’ – NEW GUIDELINES (OCT 2020)


Comprehensive care in patients with diabetes and CKD
Management of CKD in diabetes can be challenging and complex, and a multidisciplinary team should be involved (doctors, nurses, dietitians, educators, etc). Patient participation is important for self-management and to participate in shared decision-making regarding the management plan. (Practice point).
We recommend that treatment with an angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor (ACEi) or an angiotensin II receptor blocker (ARB) be initiated in patients with diabetes, hypertension, and albuminuria, and that these medications be titrated to the highest approved dose that is tolerated (1B).
Lifestyle interventions in patients with diabetes and CKD
We suggest maintaining a protein intake of 0.8 g protein/kg)/d for those with diabetes and CKD not treated with dialysis (2C).
On the amount of proteins recommended in these guidelines, they suggest (‘recommend’ becomes a ‘suggest’ at this level of evidence) a very precise intake of 0.8g/kg/d in patients with diabetes and CKD. Lower dietary protein intake has been hypothesized but never proven to reduce glomerular hyperfiltration and slow progression of CKD, however in patients with diabetes, limiting protein intake below 0.8g/kg/d can be translated into a decreased caloric content, significant weight loss and quality of life. Malnutrition from protein and calorie deficit is possible.
Physical activity
We recommend that patients with diabetes and CKD be advised to undertake moderate-intensity physical activity for a cumulative duration of at least 150 minutes per week, or to a level compatible with their cardiovascular and physical tolerance (1D).
INFOGRAPHIC: ‘WHAT IS HERD IMMUNITY?’ – ACHIEVING IT WITH COVID-19 (JAMA)
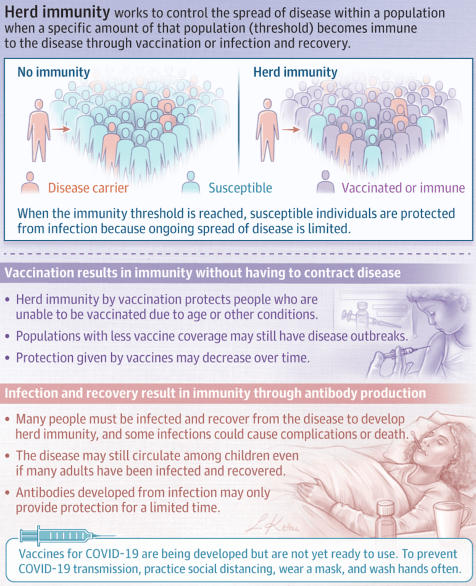
What Is Herd Immunity?
Herd immunity occurs when a significant portion of a population becomes immune to an infectious disease, limiting further disease spread.
Disease spread occurs when some proportion of a population is susceptible to the disease. Herd immunity occurs when a significant portion of a population becomes immune to an infectious disease and the risk of spread from person to person decreases; those who are not immune are indirectly protected because ongoing disease spread is very small.
The proportion of a population who must be immune to achieve herd immunity varies by disease. For example, a disease that is very contagious, such as measles, requires more than 95% of the population to be immune to stop sustained disease transmission and achieve herd immunity.
How Is Herd Immunity Achieved?
Herd immunity may be achieved either through infection and recovery or by vaccination. Vaccination creates immunity without having to contract a disease. Herd immunity also protects those who are unable to be vaccinated, such as newborns and immunocompromised people, because the disease spread within the population is very limited. Communities with lower vaccine coverage may have outbreaks of vaccine-preventable diseases because the proportion of people who are vaccinated is below the necessary herd immunity threshold. In addition, the protection offered by vaccines may wane over time, requiring repeat vaccination.
Achieving herd immunity through infection relies on enough people being infected with the disease and recovering from it, during which they develop antibodies against future infection. In some situations, even if a large proportion of adults have developed immunity after prior infection, the disease may still circulate among children. In addition, antibodies from a prior infection may only provide protection for a limited duration.
People who do not have immunity to a disease may still contract an infectious disease and have severe consequences of that disease even when herd immunity is very high. Herd immunity reduces the risk of getting a disease but does not prevent it for nonimmune people.
Herd Immunity and COVID-19
There is no effective vaccine against coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) yet, although several are currently in development. It is not yet known if having this disease confers immunity to future infection, and if so, for how long. A large proportion of people would likely need to be infected and recover to achieve herd immunity; however, this situation could overwhelm the health care system and lead to many deaths and complications. To prevent disease transmission, keep distance between yourself and others, wash your hands often with soap and water or sanitizer that contains at least 60% alcohol, and wear a face covering in public spaces where it is difficult to avoid close contact with others.
INFOGRAPHIC: ‘STOP THE SUPERSPREADING TO STOP THE COVID-19 PANDEMIC’











