A year ago, we estimated that up to $250 billion of US healthcare spend could potentially be shifted to virtual or virtually enabled care. Approaching this potential level of virtual health is not a foregone conclusion. It would likely require sustained consumer and clinician adoption and accelerated redesign of care pathways to incorporate virtual modalities.
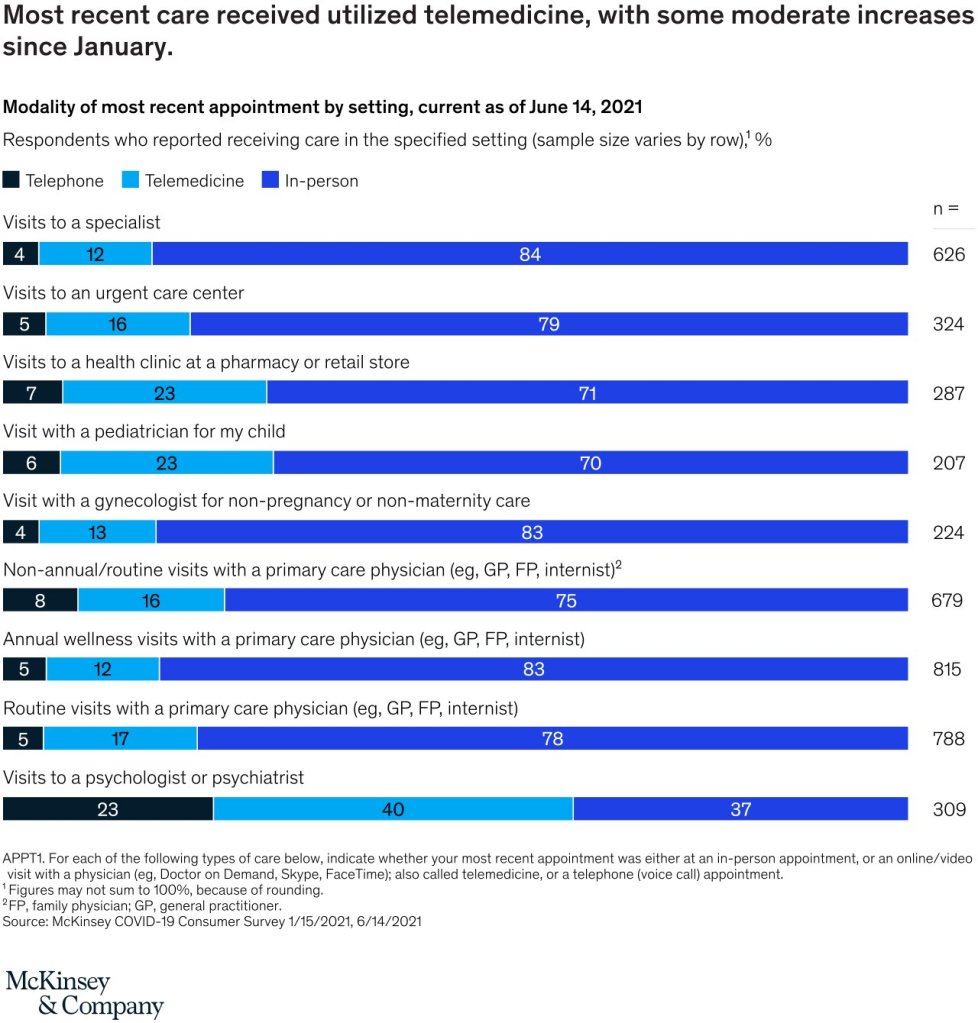
- Telehealth utilization has stabilized at levels 38X higher than before the pandemic. After an initial spike to more than 32 percent of office and outpatient visits occurring via telehealth in April 2020, utilization levels have largely stabilized, ranging from 13 to 17 percent across all specialties.2 This utilization reflects more than two-thirds of what we anticipated as visits that could be virtualized.3
- Similarly, consumer and provider attitudes toward telehealth have improved since the pre-COVID-19 era. Perceptions and usage have dropped slightly since the peak in spring 2020. Some barriers—such as perceptions of technology security—remain to be addressed to sustain consumer and provider virtual health adoption, and models are likely to evolve to optimize hybrid virtual and in-person care delivery.
- Some regulatory changes that facilitated expanded use of telehealth have been made permanent, for example, the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services’ expansion of reimbursable telehealth codes for the 2021 physician fee schedule. But uncertainty still exists as to the fate of other services that may lose their waiver status when the public health emergency ends.
- Investment in virtual care and digital health more broadly has skyrocketed, fueling further innovation, with 3X the level of venture capitalist digital health investment in 2020 than it had in 2017.4
- Virtual healthcare models and business models are evolving and proliferating, moving from purely “virtual urgent care” to a range of services enabling longitudinal virtual care, integration of telehealth with other virtual health solutions, and hybrid virtual/in-person care models, with the potential to improve consumer experience/convenience, access, outcomes, and affordability.