What is the difference between intraoperative radiation therapy and normal radiation? Is radiation a standard treatment option, or are there other approaches?
 Mayo Clinic (March 28, 2023):
Mayo Clinic (March 28, 2023):
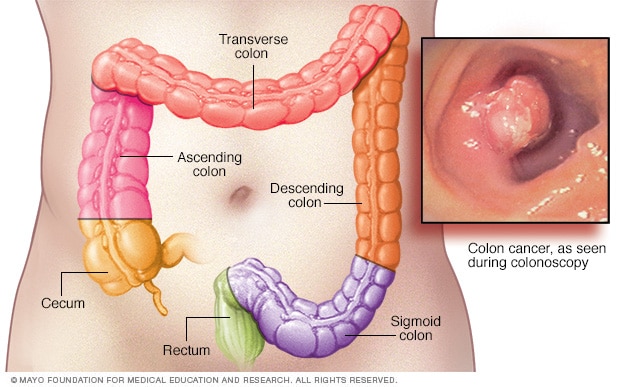
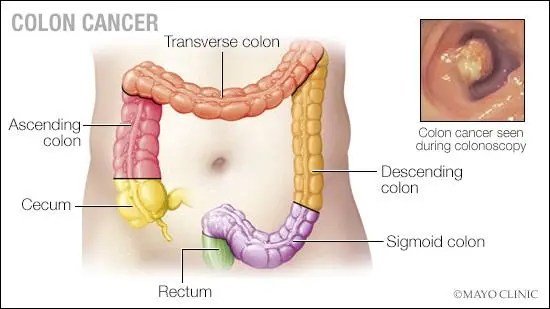
ANSWER: Colon cancer is one of the most common malignancies in the U.S., with more than 100,000 new cases diagnosed each year. Over a lifetime, it is estimated that 1 in 23 men and 1 in 26 women will be diagnosed with colon cancer. Typical colon cancers start as a polyp-like growth in the inside layer of the colon, which can be seen during a colonoscopy. Most cancer organizations recommend starting colonoscopy screenings at age 45.
When the treatment team is concerned about achieving negative margins, or removing the entire tumor with an edge of normal tissue around the specimen, intraoperative radiation therapy may be considered. Intraoperative radiation therapy rarely is used for colon cancer, but, when necessary, the area of concern is directly targeted with a single fraction of radiation during surgery.
When a mass is found during a colonoscopy or cancer is suspected, biopsies are taken and reviewed by a pathologist. In this scenario, most patients are asymptomatic. Without preventive colon cancer screenings, a tumor may grow to an advanced stage before it causes any symptoms that a patient or health care professional would recognize. The most common signs and symptoms of colon cancer are anemia, which may lead to fatigue; abdominal pain; blood in the stool or other bowel changes; weight loss; and signs of obstruction.
Once colon cancer is diagnosed, the next step is a staging examination. This involves a history and physical examination; blood work; confirmation that a full colonoscopy has been performed; and CT scans of the chest, abdomen and pelvis. The results of these tests will allow your health care professional to assign a clinical stage. In stages 1 and 2, the tumor remains in the colon wall with no evidence that it has spread further. With stage 3, there is concern that the tumor cells have spread to the regional lymph nodes, and in stage 4 colon cancer, the tumor cells have spread outside of the local area to other organs — most commonly the liver, lungs or peritoneum.
Surgery is the mainstay of treatment for stages 1, 2 and 3 disease and is usually the first step in the treatment process. The segment of the colon bearing the tumor is removed, along with the draining lymph nodes. The ends of the intestine are reconnected, and the specimen is sent to the pathologist who then performs a histologic examination of the colon and the associated lymph nodes. The pathologist will assign a final pathologic stage to the tumor, which will dictate the need for any additional treatment.
Scripps Research (April 11, 2023) – From smartwatches and fitness bands to glucose monitors and in-home ultrasounds, the proliferation of digital devices is igniting a revolution in healthcare and medical research.