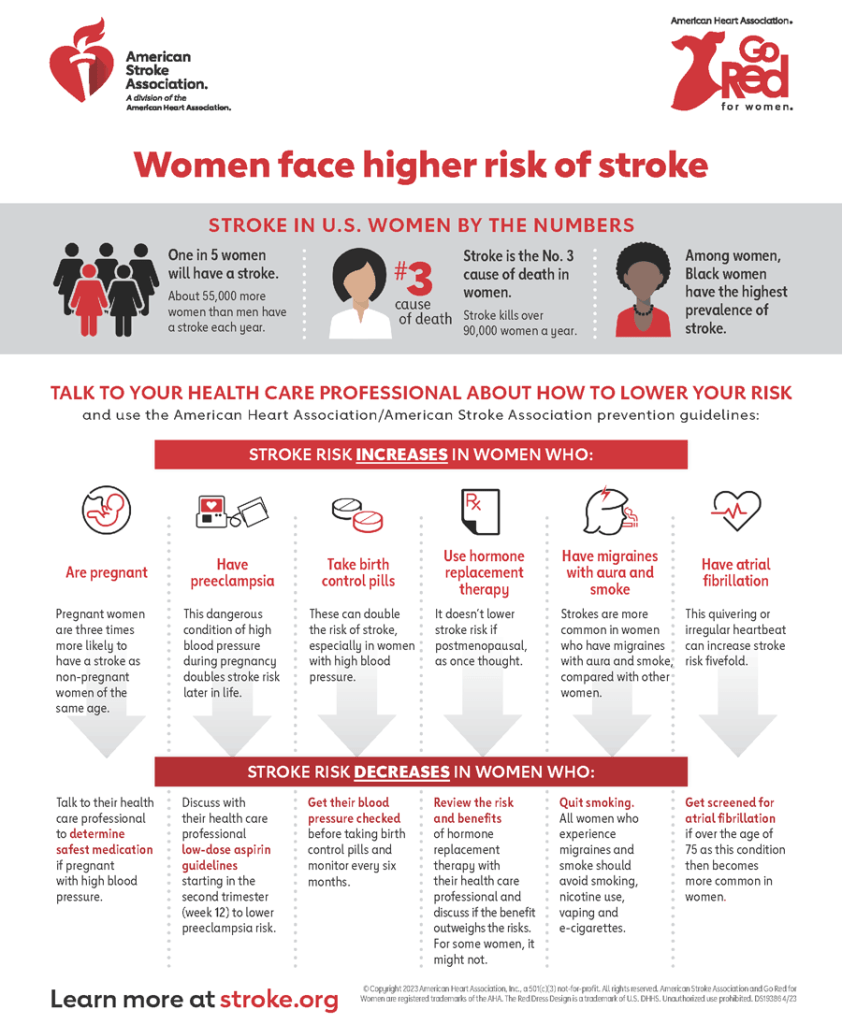
Stroke in U.S. Women by the Numbers
One in 5 women will have a stroke. About 55,000 more women than men have a stroke each year.
Stroke is the No. 3 cause of death in women. Stroke kills over 90,000 women a year.
Among women, Black Women have the highest prevalence of stroke.
Talk to your health care provider about how to lower your risk and use the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association prevention guidelines:
Stroke risk increases in women who:
- Are pregnant. Pregnant women are three times more likely to have a stroke as women of the same age.
- Have preeclampsia. This dangerous condition of high blood pressure during pregnancy doubles stroke risk later in life.
- Take birth control pills. These can double the risk of stroke, especially in women with high blood pressure.
- Use hormone replacement therapy. It doesn’t lower it, like once thought.
- Have migraines with aura and smoke. Strokes are more common in women who have migraines with aura and smoke, compared with other women.
- Have atrial fibrillation. This quivering or irregular heartbeat can increase stroke risk fivefold. After age 75, it’s more common in women than men.
Stroke risk decreases in women who:
- Talk to their health care provider to determine safest medication if pregnant with high blood pressure.
- Discuss with their health care provider low-dose aspirin guidelines starting in the second trimester (week 12) to lower preeclampsia risk.
- Get their blood pressure checked before taking birth control pills and monitor every six months.
- Don’t use hormone replacement therapy to prevent stroke if postmenopausal.
- Quit smoking if they have migraines with aura.
- Get screened for atrial fibrillation if over age 75.