Peripheral Neuropathy is a common problem, and almost a quarter of the population will eventually suffer from it. It is very common in diabetes and metabolic syndrome, alcoholism, and in cancer therapy.
Even getting older is a risk; almost 10% of individuals 65 years old have some symptoms. There are more than 100 different types of peripheral neuropathy, and often it is just one feature of a primary illness.
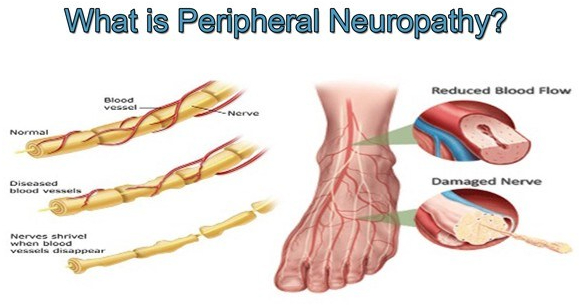
Sometimes there is no known cause, such as in 2 of my older friends. I have a diminished vibratory sense in my feet, which causes me no noticeable problem. The longer nerves are more likely to be involved, except for the rare sensory ganglionopathy which is symptomatic of some cancers ( a “paraneoplastic disorder”) , some infections and autoimmune diseases.
When the sensory ganglia are involved, the numbness, tingling or pain can be more central, such as in the face or upper arm. There are 3 types of nerves that can be involved in peripheral neuropathy; Sensory, Motor and autonomic.
The sensory nerves deal with sensations, such as hot, cold, touch, pain, tingling, and numbness. Motor nerve involvement results in weakness or paralysis of an arm, leg or other area under Voluntary control. The autonomic nervous system coordinates activities beyond voluntary control, such as sweating, salivation, food propulsion and heart rate, which can be activated or inhibited.
The symptoms of neuropathy depend upon the type of nerve involved. Balance is a complex ability that can be disturbed by a lack of proper sensory nerve function (Position sense or proprioception) motor weakness, vision or coordination which involve higher centers.
The medical evaluation of peripheral neuropathy begins with a family practitioner or internist who does a detailed history, asking about such things as diet, medications, alcohol consumption, and injuries. Vitamin intake is important, but can be overdone.
Peripheral nerve symptoms can actually be caused by excessive B6, pyridoxine. The upper limit is 100 Mg.. A physical exam checks for weakness, sensory problems, reflexes and balance. Blood tests may reveal diabetic, kidney, liver, thyroid or immune problems problems.
A major disorder associated with neuropathy may be revealed and pursued. If nothing turns up, and the neuropathy is significant, referral may be needed to a neurologist, or other appropriate specialist. Many specialized tests and treatments may be needed.
Even with the best of care, a specific “cure” may not be found. Peripheral neuropathy can often be avoided by a healthy lifestyle.