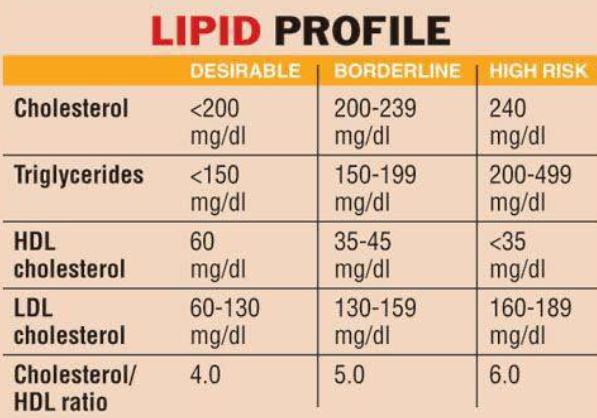
NSAIDs are a common pain medication. Younger people with no underlying diseases take them all the time for headaches, sprained ankles, and other injuries.

I have an underlying stomach problem that makes me want to minimize the gastrointestinal side effects when I need an NSAID medication, and for that reason I have 100 mg Celebrex, or celecoxib in my medicine cabinet.
I am fortunate not to have much severe pain, although I do have osteoarthritis in my hand, and infrequent abdominal pain from a small bowel surgery.
Celebrex is my magic bullet whenever I have pain from diverse causes such as in my legs; I do have a very active exercise program of an hour a day in the morning and a half an hour in the evening.
The Cox 2 inhibitor‘s were initially touted as being able to avoid the stomach problems caused by the non-selective NSAIDs. Unfortunately, several of them, such as vioxx, were associated with more heart attacks, a 45% increase, and they were removed from the market . Celebrex was a survivor from this group, but it still tends to cause an increase in blood pressure.
Whenever you take any medication, it’s always a trade-off; relief from the problem at hand, traded for the inevitable side effects. There is no powerful medication that has only the desired activity, and most people are better off with a healthy lifestyle than taking medication.
Another advantage with medication avoidance is that when you take the medication, it tends to work a whole lot better. At least I have found that to be true, and celecoxib is my magic pain medication, which has salvaged countless nights of sleep.