One out of five people experience hives in their lifetime. These are itchy bumps, which are surrounded by a field of redness, and itch like crazy.
Hives are caused by the release of histamine from mast cells in the tissues, or basophiles in the bloodstream.
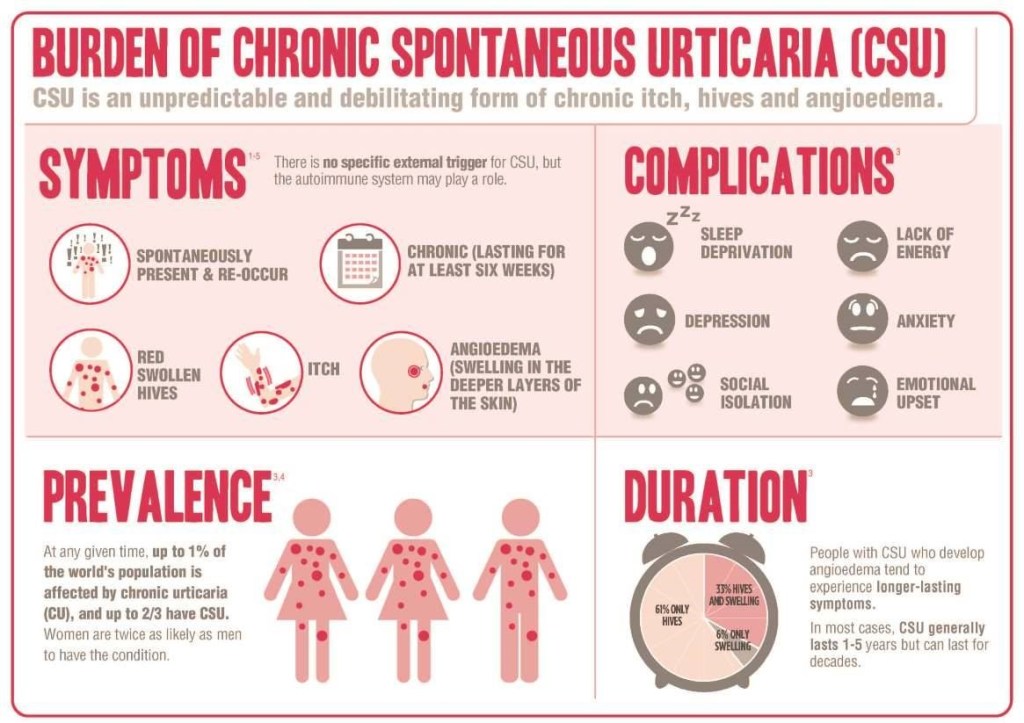
Itching is the chief annoyance, which can cause sleep loss, as well as misery severe enough to distract from normal activities. Hives are sometimes associated with angioedema, which is swelling in certain areas, such as the throat and windpipe, which can be fatal. Extensive hives, with leaking of fluid out of the blood vessel’s can also cause low blood pressure, which can be fatal, especially if you’re in a precarious situation, such as swimming.
The topic has been increasingly understood, and therefore growing increasingly complex, and I will only touch on some high points. I would recommend the review of Dermnet from New Zealand, which is included below if you want more complete and reasonably understandable information.
I have had hives only one time, after being stung by a bee for the third or fourth time. Within a few seconds, I started itching all over my body, but had no dizziness so apparently didn’t lose much fluid from my blood vessels. The hives went away after taking an antihistamine. I sometimes get itchy after wearing a tight belt, which is probably caused by histamine release due to “ pressure urticaria. As mentioned in previous articles, I also get itchy skin without hives if I let my skin get too dry, helped by lubricants, and have itchy ears for which I take drops of mineral oil into my ears, and wash the wax out every few months.
Urticaria, or hives, can be in a limited area or all over the body, can last a few days or come and go indefinitely, and can be mild or incapacitating. They can be caused by a huge variety of known things, from infections, such as upper respiratory infections, foods such as peanut, drugs such as antibiotics, contactants, such as latex gloves, and stings or other injectants, which can generalize into severe and sometimes fatal anaphylaxis.
Adrenaline, and antihistamines, are needed immediately in these situations. You may have heard of the rapidly injectable EpiPen, which you must carry with you if at risk.
Often with chronic urticaria, the cause remains unknown or “idiopathic”. As an allergist, this used to drive me almost as crazy as my patients, A lot of progress has been made in the last few decades. About half of the unknown causes turns out to be antibodies directed towards the allergic antibody, IGE, which can be treated by yet another antibody, omalizumab, or some other expensive new medications.
If you have urticaria that continues, and interferes with your enjoyment of life, You can help your doctor out by carefully remembering the circumstances, under which the hives occur, and the places on your body where they are the most annoying. Ask your relatives if they have any autoimmune diseases, like lupus, or vitiligo. Know exactly what medication you are taking, and bring a list with you.
Angioedema can be fatal due to blockage of breathing and demands immediate attention. ACE Inhibitors can cause these swellings, which often occur without itching.
Once again, go to the excellent and understandable article by Dermnet/urticaria/an overview.
—Dr. C.