Gonorrhea been present since the earliest times. The United States has one of the highest incidences, and it was very common in colonial America, where it was called “clap”. Adolescents, with their increased sexual activity, have the highest incidence, and girls are somewhat more likely to have it than boys.
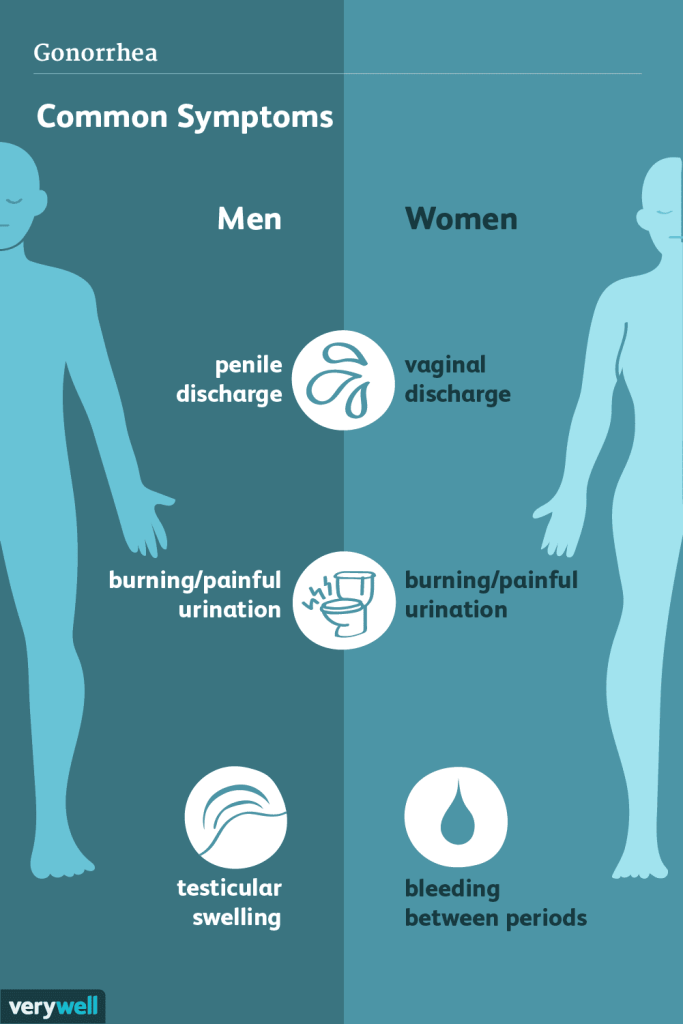
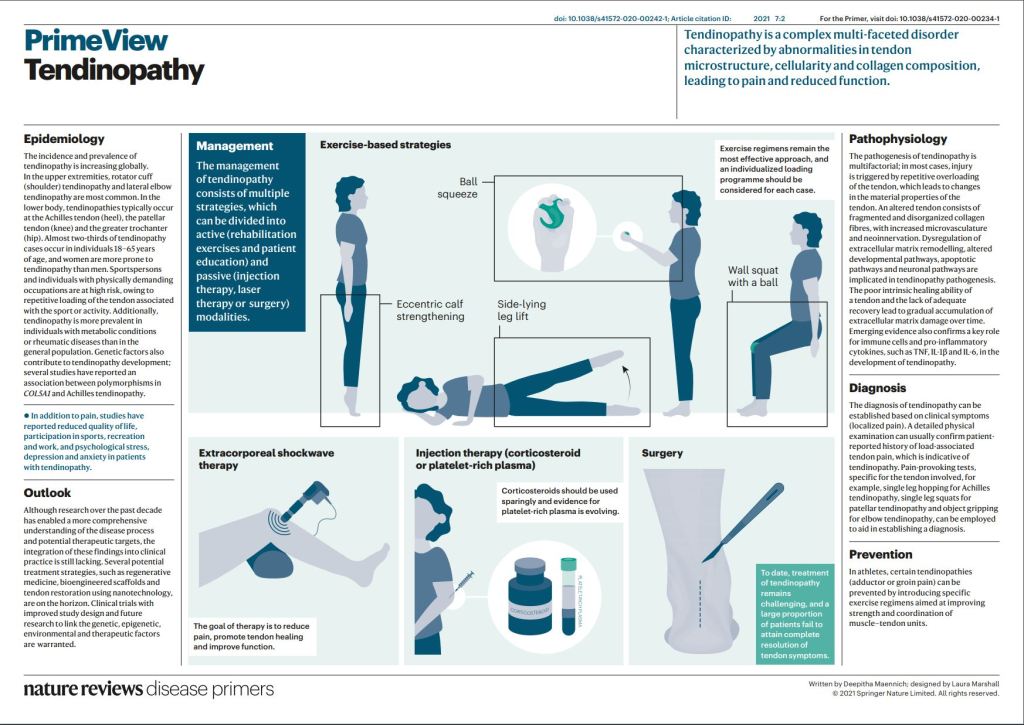
The symptoms have to do with infection and inflammation of the urethra. Burning on urination is almost universal, and purulent discharge and presence of pus in the urine is frequent. The infection is mostly a nuisance, but it can travel up the genito-urinary tract, and into the spermatic ducts in the male or the fallopian tubes in the female, and it is a common cause of sterility and pelvic inflammatory disease, or PID.
With its high frequency in young females, bacterial ointments are routinely applied to the eyes of newborn babies to prevent severe infection and possible blindness.
When I was practicing medicine, the diagnosis was made by culturing for the bacterium neisseria gonorrhea. Now the NAAT, the nucleic acid amplification test, is the gold standard.
In my practicing days, penicillin was the magic bullet, but resistance he has developed so that a cephalosporin and azithromycin combination is currently used.
STDs, sexually transmitted diseases, are one of the commonest conditions encountered in student health, according to a good friend.
Please refer to the attached Mayo Clinic article for more information.
—Dr. C.