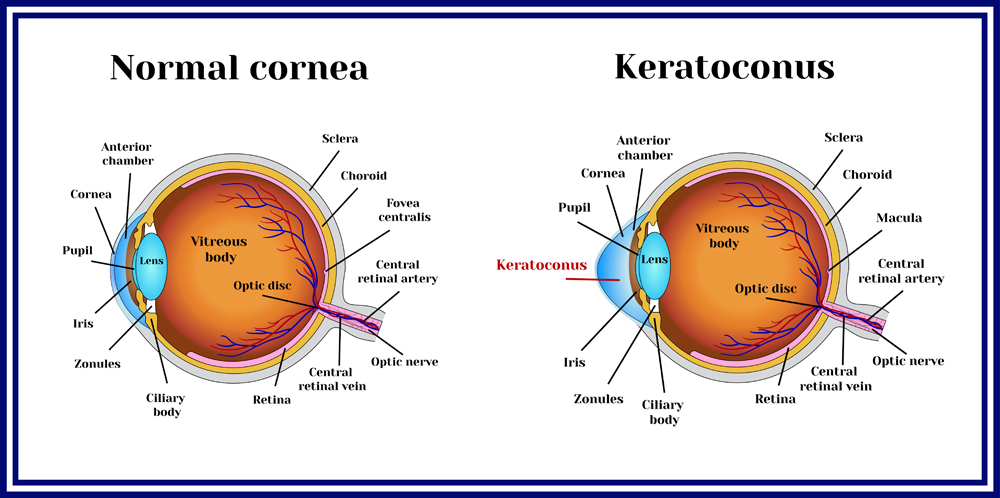
Herpetic Keratitis is a viral infection of the transparent, frontmost part of the eye, the cornea.
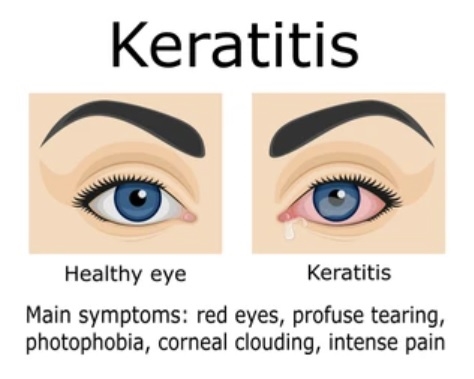
Herpes 1 or 2 when rubbed into the eye from a cold sore, or contacted from somebody else with herpes, will often affect the cornea. The use of corticosteroid eyedrops or ointment will allow the disease to spread faster.
The symptoms are pain and redness of the eye and are a medical emergency, needing prompt treatment by your doctor to prevent scarring and blindness.
Antiviral eyedrops, such as valacyclovir, are used to treat ophthalmic herpes.
A related condition is ophthalmic zoster, caused by the varicella zoster virus. The VZ virus will produce chickenpox in unimmunized people, go into dormancy in the nervous system, and then resurface, if immunity wanes, as shingles. If the shingles occurs in the ophthalmic division of the trigeminal nerve, affecting the skin near the eye, the cornea will often be involved. Ophthalmic zoster is also treated by antiviral eyedrops.
The varicella zoster virus is closely related to the herpes simplex virus, and is a member of the same nasty family of viruses.
—Dr. C.