From a New York Times article (May 5, 2020):
“Calling my patients at home, with or without video, has become my new normal. After 25 years of being a pediatrician, telemedicine is teaching me new ways to communicate with families.“
“I try to hear the mother above the babbling of her baby. And then to listen to the babbling of the baby. Is it joyful? Are there big breaths between the babbling?“
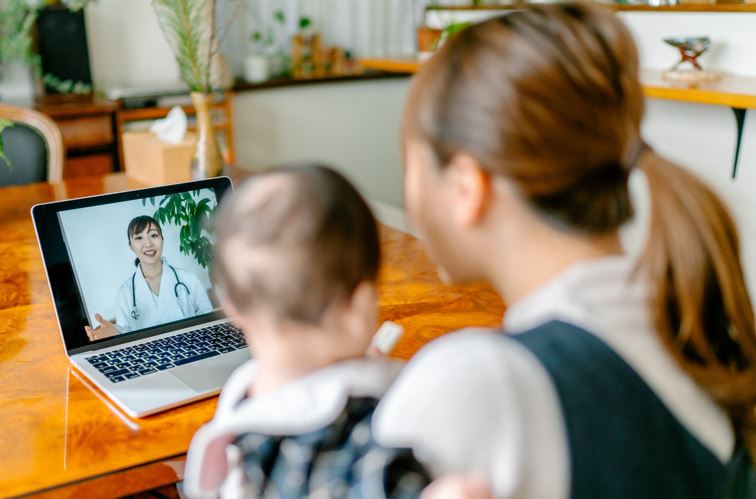

A federal government waiver, issued early in March, expanded the use of federally funded health insurance — Medicaid, Medicare and the Children’s Health Insurance Program — to pay for telemedicine visits. The goal was to allow more people with symptoms of illness to be heard, and sometimes also seen, by a health care provider without the risk of exposure to coronavirus at a doctor’s office or hospital.
The federal government has been expanding the use of telemedicine for years — but like so many changes in this pandemic, what used to take years to transform, we are now doing within weeks.