Hypertensive eye disease is diagnosed on the basis of a clinical history of #Hypertension and the presence of relevant pathological changes in the eye that are observed via fundoscopy or imaging. https://go.nature.com/3t0PahO
Commentary:
Control of hypertension is one of the triumphs of modern medicine, and there are many effective medications. One of the main problems that I hear about has to do with taking too much of the medication, and having dizziness, especially on standing, which could cause a fall and injuries.
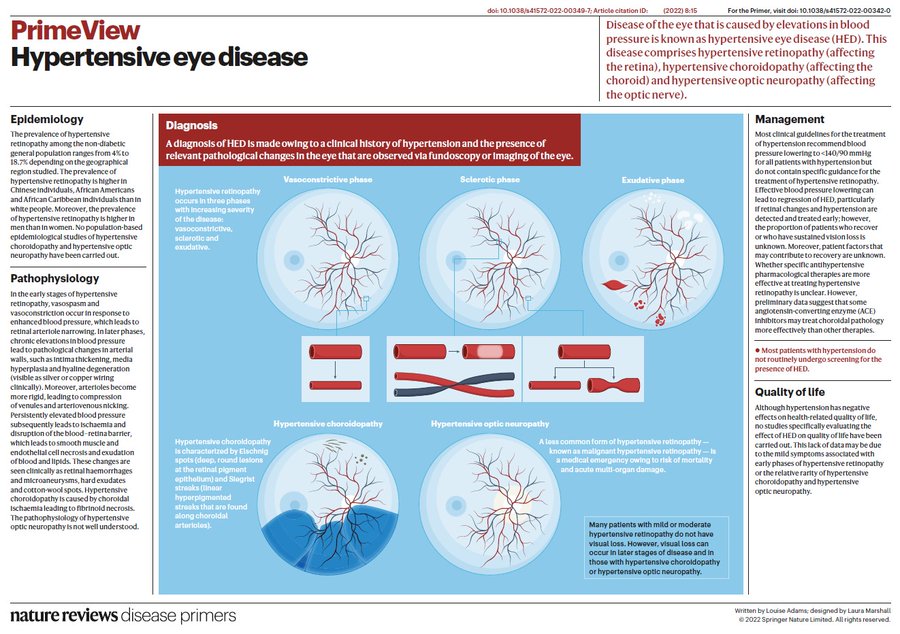
Abnormalities of the eye with hypertension are common. the doctor can look directly at the bare blood vessels as they course along the back of the eye. A hypertensive artery passing over a vein in the eye compresses it, producing a “nick” that doctors look for. other findings are shown in the info graphic.
These findings help doctors make a diagnosis, but only the rare complications of hypertensive optic atrophy and Choroidopathy actually endanger the vision.
The main organ that seems to suffer the most from hypertension is the heart, which has to work against a heavy load to pump the blood effectively at high pressure. This thickens the walls of the heart, especially the left side, making it less effective. Enlargement of the heart, heart attacks, and heart failure are not uncommon.
The brain is at risk with hypertensive arterial disease, and strokes can be a problem.
Kidney failure is also a real worry.
When you see your doctor for a blood pressure reading, make sure to take off coats and long sleeves. so that the bare arm can be tested. The left arm In right-handed people is preferable, because it has less musculature to shield the artery from compression by the blood pressure cuff.
Be sure you take your medication, if prescribed. The main emergency room visits occasioned by high blood pressure, such as 180/110, is when the patient skips the medication.
—Dr. C.